Dependency
There are two main topics in package dependency, the dependency itself, and reverse dependency. Beside these two, there are other topic as well, such as managing conflict that we do not cover here.
Dependency
Package that required by: such as man-db need groff-base and other.
This will show required parts of the package.
$ apt-cache depends man-db Almost equal to:
$ apt depends man-db
man-db
PreDepends: dpkg
Depends: groff-base
Depends: bsdmainutils
|...
Suggests: groff
Suggests: less
Suggests: <www-browser>
...
lynx
...
Replaces: <man>
man-db
...
Replaces: <nlsutils>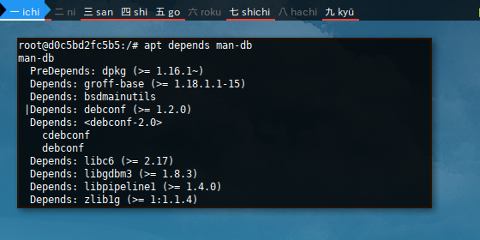
This apt show provide dependency too.
$ apt show man-db
root@d0c5bd2fc5b5:/# apt show man-db
...
Depends: groff-base (>= 1.18.1.1-15), bsdmainutils, debconf (>= 1.2.0) | debconf-2.0, libc6 (>= 2.17), libgdbm3 (>= 1.8.3), libpipeline1 (>= 1.4.0), zlib1g (>= 1:1.1.4)
...aptitude search also works too.
$ aptitude search ~Rman-db
i A bsdmainutils - collection of more utilities from F
p cdebconf - Debian Configuration Management Sys
i A debconf - Debian configuration management sys
v debconf-2.0 -
i A dpkg - Debian package management system
i A groff-base - GNU troff text-formatting system (b
i A libc6 - GNU C Library: Shared libraries
i A libgdbm3 - GNU dbm database routines (runtime
i A libpipeline1 - pipeline manipulation library
i A zlib1g - compression library - runtime 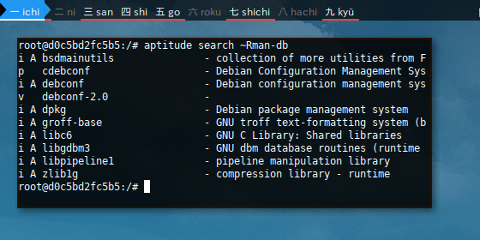
Reverse Dependency
Package that require: such as groff-base needed by man-db or other.
$ apt-cache rdepends groff-base Almost equal to:
$ apt rdepends groff-base
groff-base
Reverse Depends:
Depends: man-db (>= 1.18.1.1-15)
Suggests: imagemagick-6.q16hdri
Suggests: imagemagick-6.q16
Recommends: rpmlint
Suggests: perl-doc
Replaces: groff (<< 1.17.2-9)
Suggests: imagemagick-6.q16hdri
Suggests: imagemagick-6.q16
Depends: groff (= 1.22.3-9)
Suggests: bioperl
Recommends: gdisk
Recommends: debian-el
Recommends: doclifter
Depends: cppman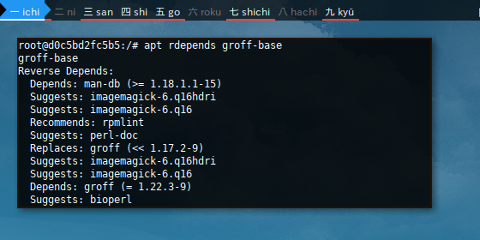
aptitude search also works too.
$ aptitude search ~Dgroff-base
p cppman - C++ 98/11 manual pages for Linux, w
p groff - GNU troff text-formatting system
i man-db - on-line manual pager 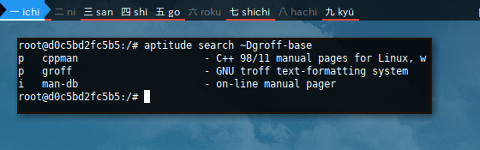
This aptitude why also provide reverse dependency.
$ aptitude why groff-base
i man-db Depends groff-base (>= 1.18.1.1-15)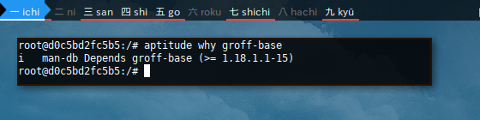
Test
Removing groff-base would remove man-db.
$ apt remove groff-base
Reading package lists... Done
Building dependency tree
Reading state information... Done
The following package was automatically installed and is no longer required:
libpipeline1
Use 'apt autoremove' to remove it.
The following packages will be REMOVED:
groff-base man-db
0 upgraded, 0 newly installed, 2 to remove and 0 not upgraded.
After this operation, 5624 kB disk space will be freed.
Do you want to continue? [Y/n]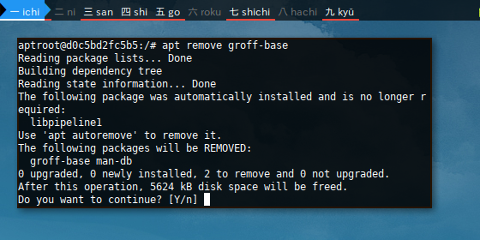
Dotty
there are also graphviz output named dotty
$ apt-cache -o APT::Cache::GivenOnly=1 dotty groff-base
digraph packages {
concentrate=true;
size="30,40";
"groff-base" -> "libc6";
"groff-base" -> "libgcc1";
"groff-base" -> "libstdc++6";
"groff-base" -> "groff"[color=springgreen];
"groff-base" -> "jgroff"[color=springgreen];
"groff-base" -> "pmake"[color=springgreen];
"groff-base" -> "troffcvt"[color=springgreen];
"pmake" [color=orange,shape=diamond];
"libc6" [color=orange,shape=box];
"libgcc1" [color=orange,shape=box];
"groff-base" [shape=box];
"groff" [color=orange,shape=box];
"troffcvt" [color=orange,shape=box];
"libstdc++6" [color=orange,shape=box];
"jgroff" [shape=triangle];
}
$ dot -Tpng groff-base.dot > groff-base.png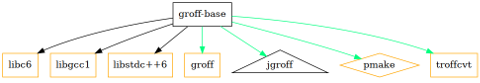
Repository
Switch repository in Debian based is simple.
Configuration
Most of the time I manage repository using
sources.list
configuration directly in Debian based distribution.
I don’t know if there is better way.
$ cat /etc/apt/sources.list
deb http://deb.debian.org/debian stretch main
deb http://deb.debian.org/debian stretch-updates main
deb http://security.debian.org stretch/updates main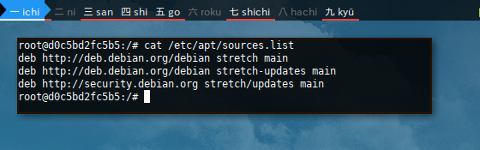
Case: Other derivation may use different repository.
deb http://auto.mirror.devuan.org/merged jessie main
deb http://auto.mirror.devuan.org/merged jessie-updates main
deb http://auto.mirror.devuan.org/merged jessie-security main
deb http://auto.mirror.devuan.org/merged ascii mainCase: Sometimes there is additional PPA as well,
inside /etc/apt/sources.list.d/ directory.
deb http://ppa.launchpad.net/wagungs/kali-linux2/ubuntu raring main
deb-src http://ppa.launchpad.net/wagungs/kali-linux2/ubuntu raring main
deb http://ppa.launchpad.net/wagungs/kali-linux/ubuntu raring main
deb-src http://ppa.launchpad.net/wagungs/kali-linux/ubuntu raring mainPolicy
However if you insist using command line,
you can get a list anyway by using apt-cache policy
$ apt policy
Package files:
100 /var/lib/dpkg/status
release a=now
500 http://security.debian.org stretch/updates/main amd64 Packages
release v=9,o=Debian,a=stable,n=stretch,l=Debian-Security,c=main,b=amd64
origin security.debian.org
500 http://deb.debian.org/debian stretch-updates/main amd64 Packages
release o=Debian,a=stable-updates,n=stretch-updates,l=Debian,c=main,b=amd64
origin deb.debian.org
500 http://deb.debian.org/debian stretch/main amd64 Packages
release v=9.1,o=Debian,a=stable,n=stretch,l=Debian,c=main,b=amd64
origin deb.debian.org
Pinned packages: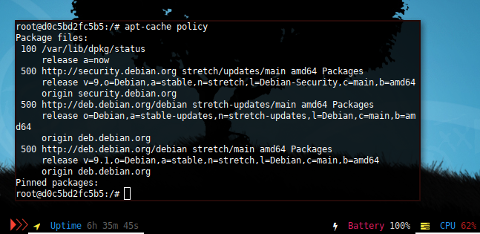
Add Repository
This require a few steps.
(1) Append the repository to /etc/apt/sources.list. I usually utilize text editor.
(2) Add the repository key to the machine, if needed such as in PPA case.
Or maybe using apt-key if necessary.
(3) Do not forget to apt update to refresh.
Note that Ubuntu based have this add-apt-repository command.
Mirror
Consider change our repository to nearest local server such as university.
$ nano /etc/apt/sources.list
deb http://kambing.ui.ac.id/debian stretch main
deb http://kambing.ui.ac.id/debian stretch-updates main
deb http://security.debian.org stretch/updates main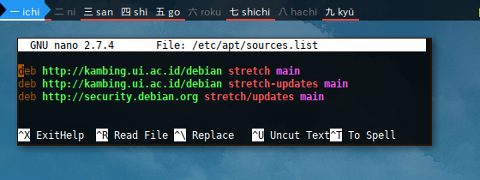
No need any repository key. We can update directly.
$ apt update
Ign:1 http://kambing.ui.ac.id/debian stretch InRelease
Get:2 http://kambing.ui.ac.id/debian stretch-updates InRelease [91.0 kB]
Get:3 http://kambing.ui.ac.id/debian stretch Release [118 kB]
Hit:4 http://security.debian.org stretch/updates InRelease
Get:5 http://kambing.ui.ac.id/debian stretch-updates/main amd64 Packages [5553 B]
Get:6 http://kambing.ui.ac.id/debian stretch Release.gpg [2373 B]
Get:7 http://kambing.ui.ac.id/debian stretch/main amd64 Packages [9497 kB]
Fetched 9714 kB in 47s (205 kB/s)
Reading package lists... Done
Building dependency tree
Reading state information... Done
All packages are up to date.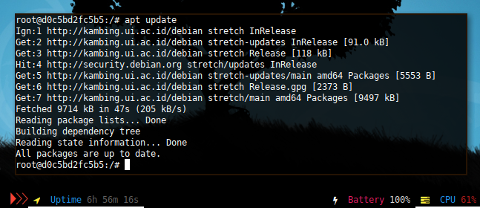
Distribution Upgrade
There are cases that a system need more than upgrade,
such as migrating python from python2 to python3,
or ncurse case, especially when many application involved.
Switching from one release to other release
require dist-upgrade.
I have never had issue with Debian,
but I experienced issues in Debian derivatives.
No need to dist-upgrade in rolling release
Now consider pulling oldstable jessie container.
$ docker pull debian:jessie
jessie: Pulling from library/debian
aa18ad1a0d33: Pull complete
Digest: sha256:f31c837c5dda4c4730a6f1189c9ae39031e966410d7b0885863bd6c43b5ff281
Status: Downloaded newer image for debian:jessie
$ docker run -it debian:jessie
root@0bf84cd70449:/#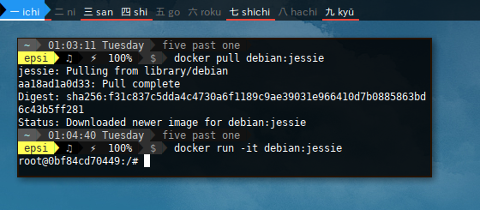
And do some basic task so that we can edit sources.list.
$ apt update
$ apt upgrade
$ apt install man-db nano less vim wget curl sudoFrom Jessie
$ nano /etc/apt/sources.list
deb http://deb.debian.org/debian jessie main
deb http://deb.debian.org/debian jessie-updates main
deb http://security.debian.org jessie/updates main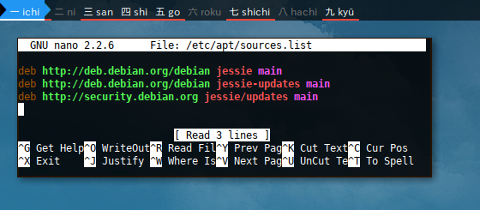
To Stretch
$ cat /etc/apt/sources.list
deb http://deb.debian.org/debian stretch main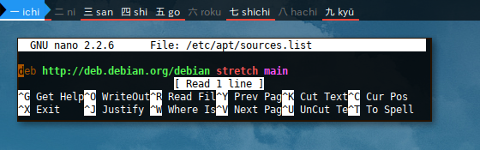
Do not forget to update.
$ apt update
...
132 packages can be upgraded. Run 'apt list --upgradable' to see them.And dist-upgrade.
$ apt dist-upgrade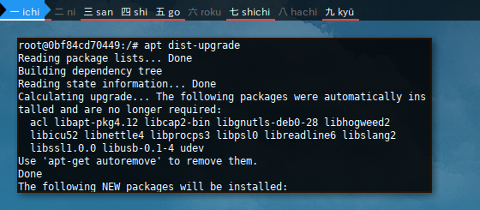
This example above using minimal install,
in this case upgrade is sufficient
and the same result with dist-upgrade.
Nothing to worry about, the command finished successfully.
Repository Pinning
Sometimes we need a package from unstable repository. There are few reason, such as trying latest version, or such version has not available yet in testing or stable. I did when I curious about tomahawk while it was just landed in_unstable_. Do not be afraid to do this as long you do not mess with system packages.
nmap Case
Consider have a look at this nmap case.
nmap has different version for stable and unstable.
-
https://packages.debian.org/search?keywords=nmap
-
stretch (stable): 7.40-1
-
sid (unstable): 7.60-1
nmap from sid (unstable) can be installed in stretch (stable). Steps below.
New Docker for Stretch
Ww need a new docker,
because we use stable release for nmap.
Now update and upgrade silently using -qq option.
$ docker run -it debian:stretch
root:/# apt update -y -qq
1 package can be upgraded. Run 'apt list --upgradable' to see it.
root:/# apt upgrade -y -qq
The following packages will be upgraded:
libgcrypt20
1 upgraded, 0 newly installed, 0 to remove and 0 not upgraded.
Need to get 523 kB of archives.
...
Stable nmap
$ apt-get install -y -qq wget curl man-db nano less nmap$ nmap -V
Nmap version 7.40 ( https://nmap.org )
...
Pinning Unstable
We need to switch the repository, to contain both stable and unstable.
$ nano /etc/apt/sources.list$ cat /etc/apt/sources.list
deb http://deb.debian.org/debian stable main
deb http://deb.debian.org/debian unstable main
And give negative number in pinning preferences, so that this unstable repository ignored, except for direct install with target.
$ touch /etc/apt/preferences.d/unstable
$ nano /etc/apt/preferences.d/unstable$ cat /etc/apt/preferences.d/example
Package: *
Pin: release a=unstable
Pin-Priority: -10
- .
$ apt update
...
All packages are up to date.$ apt upgrade
...
0 upgraded, 0 newly installed, 0 to remove and 0 not upgraded.Make sure that system cannot be upgraded to unstable.
$ apt list --upgradable
Listing... Done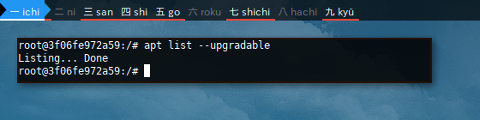
Unstable nmap
Have a look at thispolicy before we install nmap.
$ apt policy
Package files:
100 /var/lib/dpkg/status
release a=now
-10 http://deb.debian.org/debian unstable/main amd64 Packages
release o=Debian,a=unstable,n=sid,l=Debian,c=main,b=amd64
origin deb.debian.org
500 http://deb.debian.org/debian stable/main amd64 Packages
release v=9.1,o=Debian,a=stable,n=stretch,l=Debian,c=main,b=amd64
origin deb.debian.org
Pinned packages: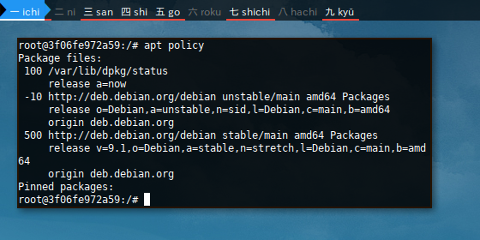
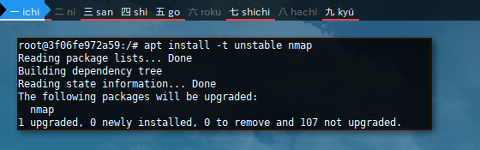
Install nmap with explicit target -t unstable.
$ apt install --target unstable nmap
Reading package lists... Done
Building dependency tree
Reading state information... Done
The following packages will be upgraded:
nmap
1 upgraded, 0 newly installed, 0 to remove and 136 not upgraded.
Need to get 5401 kB of archives.
...
$ nmap -V
Nmap version 7.60 ( https://nmap.org )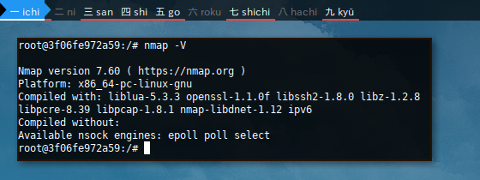
Consider examine,
have a look at the nmap version difference.
Now we have unstable package in stable system.
What’s Next
There are still, build form source topic. Consider finish reading [ Part Four ].
Thank you for reading