Preface
Goal: Examine wireless in system: device, driver, and interface.
I suddenly found out that I do not have good understanding, about relationship configuration, between device, driver and interface. I think it is time to grow up.
Table of Content
-
3: Other Tools
An Issue Behind This Article
Start from Working Machine as an Example
First December is my first day on my new office. I should work with a new notebook owned by this good company.
I have an issue I cannot solve while setting up wifi in my notebook. So I decide to examine a working wifi in my system. So that I can use my own scattered notes, to solve my notebook issue later on.
I never have any experience with third party device.
I mean driver not directly supported by kernel.
Even when I’m using Gentoo for years,
my hardware is so common,
that I don’t really need to tweak.
My working system is Mini PC using Artix. While my notebook is Lenovo. I might write another article, if could solve my notebook issue.
Because I simply don’t know how to solve.
1: Device: PCI and USB
There are a some common command in linux,
such as lsblk, lsmod, lspci, lsusb.
Devices can be found in either lsusb or lspci.
USB Devices
❯ lsusbBus 002 Device 001: ID 1d6b:0003 Linux Foundation 3.0 root hub
Bus 001 Device 004: ID 8087:0aaa Intel Corp. Bluetooth 9460/9560 Jefferson Peak (JfP)
Bus 001 Device 003: ID 046d:c077 Logitech, Inc. Mouse
Bus 001 Device 002: ID 046d:c534 Logitech, Inc. Unifying Receiver
Bus 001 Device 008: ID 0781:5567 SanDisk Corp. Cruzer Blade
Bus 001 Device 001: ID 1d6b:0002 Linux Foundation 2.0 root hub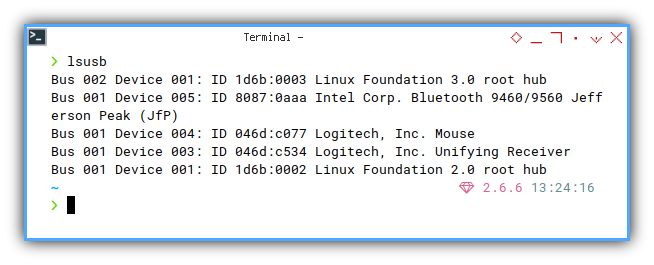
PCI Devices
❯ lspci00:00.0 Host bridge: Intel Corporation Device 4e24
00:02.0 VGA compatible controller: Intel Corporation JasperLake [UHD Graphics] (rev 01)
00:04.0 Signal processing controller: Intel Corporation Dynamic Tuning service
00:08.0 System peripheral: Intel Corporation Device 4e11
00:14.0 USB controller: Intel Corporation Device 4ded (rev 01)
00:14.2 RAM memory: Intel Corporation Device 4def (rev 01)
00:14.3 Network controller: Intel Corporation Wi-Fi 6 AX201 160MHz (rev 01)
00:15.0 Serial bus controller: Intel Corporation Serial IO I2C Host Controller (rev 01)
00:15.2 Serial bus controller: Intel Corporation Device 4dea (rev 01)
00:16.0 Communication controller: Intel Corporation Management Engine Interface (rev 01)
00:17.0 SATA controller: Intel Corporation Device 4dd3 (rev 01)
00:19.0 Serial bus controller: Intel Corporation Device 4dc5 (rev 01)
00:19.1 Serial bus controller: Intel Corporation Device 4dc6 (rev 01)
00:1a.0 SD Host controller: Intel Corporation Device 4dc4 (rev 01)
00:1c.0 PCI bridge: Intel Corporation Device 4dbc (rev 01)
00:1c.7 PCI bridge: Intel Corporation Device 4dbf (rev 01)
00:1e.0 Communication controller: Intel Corporation Device 4da8 (rev 01)
00:1e.3 Serial bus controller: Intel Corporation Device 4dab (rev 01)
00:1f.0 ISA bridge: Intel Corporation Device 4d87 (rev 01)
00:1f.3 Audio device: Intel Corporation Jasper Lake HD Audio (rev 01)
00:1f.4 SMBus: Intel Corporation Jasper Lake SMBus (rev 01)
00:1f.5 Serial bus controller: Intel Corporation Jasper Lake SPI Controller (rev 01)
01:00.0 Non-Volatile memory controller: Silicon Motion, Inc. SM2263EN/SM2263XT SSD Controller (rev 03)
02:00.0 Ethernet controller: Realtek Semiconductor Co., Ltd. RTL8111/8168/8411 PCI Express Gigabit Ethernet Controller (rev 15)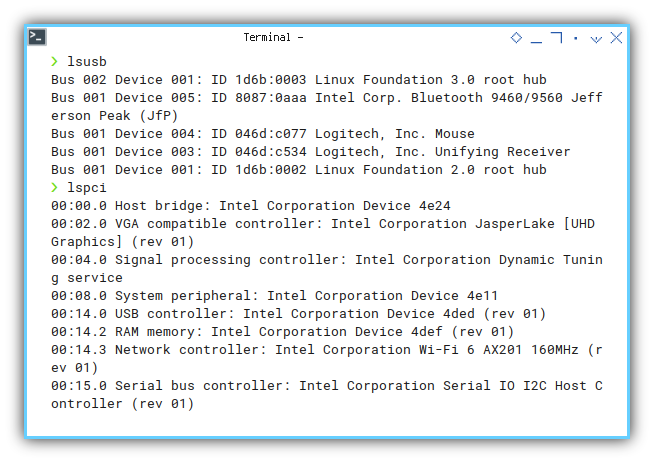
You can have a look at full image here below:
PCI Details
We can filter our query using grep.
❯ lspci | grep Network00:14.3 Network controller: Intel Corporation Wi-Fi 6 AX201 160MHz (rev 01)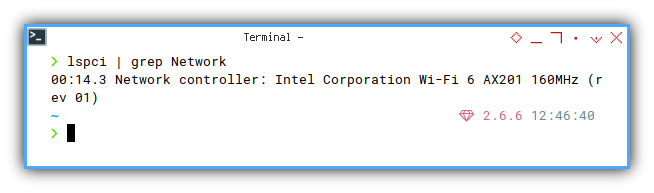
And then find the detail using the slot ID (bus:device.function).
❯ lspci -v -s 00:14.300:14.3 Network controller: Intel Corporation Wi-Fi 6 AX201 160MHz (rev 01)
Subsystem: Intel Corporation Device 02a4
Flags: bus master, fast devsel, latency 0, IRQ 16
Memory at 6001124000 (64-bit, non-prefetchable) [size=16K]
Capabilities: <access denied>
Kernel driver in use: iwlwifi
Kernel modules: iwlwifi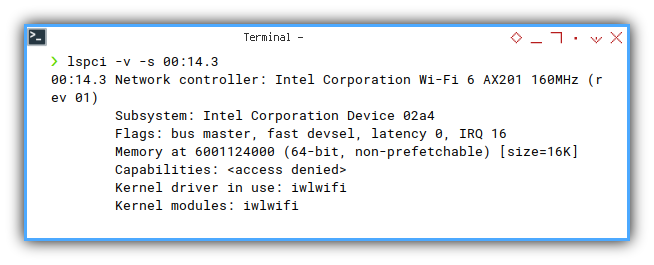
And find the kernel driver.
❯ lspci -k -s 00:14.300:14.3 Network controller: Intel Corporation Wi-Fi 6 AX201 160MHz (rev 01)
Subsystem: Intel Corporation Device 02a4
Kernel driver in use: iwlwifi
Kernel modules: iwlwifi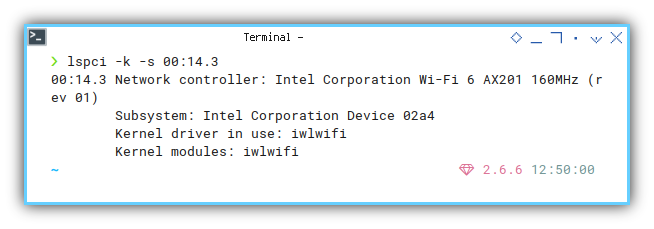
So here we have:
- Device: Intel Wi-Fi 6 AX201
- Driver:
iwlwifi
2: Interface: IP
ifconfig (obsolete)
Veteran (but dumb) like me, might familiar with this obsolete command.
❯ ifconfig wlan0wlan0: flags=-28605<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,MULTICAST,DYNAMIC> mtu 1500
inet 192.168.5.177 netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast 192.168.5.255
inet6 fe80::fa9e:94ff:fea8:775d prefixlen 64 scopeid 0x20<link>
ether f8:9e:94:a8:77:5d txqueuelen 1000 (Ethernet)
RX packets 132668 bytes 162912544 (155.3 MiB)
RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0
TX packets 33805 bytes 7959536 (7.5 MiB)
TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0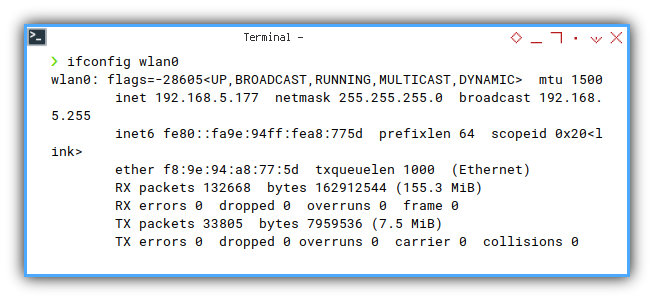
IP Link
The basic command is so simple as below:
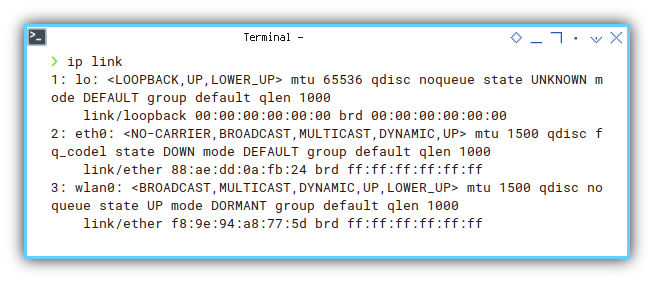
❯ ip link1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN mode DEFAULT group default qlen 1000
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
2: eth0: <NO-CARRIER,BROADCAST,MULTICAST,DYNAMIC,UP> mtu 1500 qdisc fq_codel state DOWN mode DEFAULT group default qlen 1000
link/ether 88:ae:dd:0a:fb:24 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
3: wlan0: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,DYNAMIC,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc noqueue state UP mode DORMANT group default qlen 1000
link/ether f8:9e:94:a8:77:5d brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ffAs we find wlan0 interface, we can then filter the result:
❯ ip link show wlan03: wlan0: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,DYNAMIC,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc noqueue state UP mode DORMANT group default qlen 1000
link/ether f8:9e:94:a8:77:5d brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff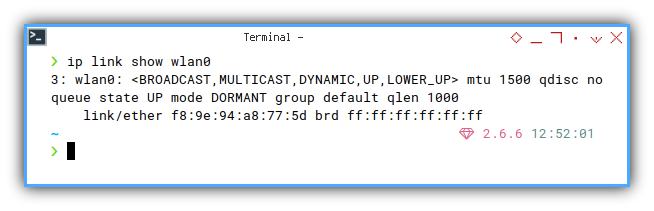
Or even show in brief, without detail.
❯ ip -br -c link showlo UNKNOWN 00:00:00:00:00:00 <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP>
eth0 DOWN 88:ae:dd:0a:fb:24 <NO-CARRIER,BROADCAST,MULTICAST,DYNAMIC,UP>
wlan0 UP f8:9e:94:a8:77:5d <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,DYNAMIC,UP,LOWER_UP> 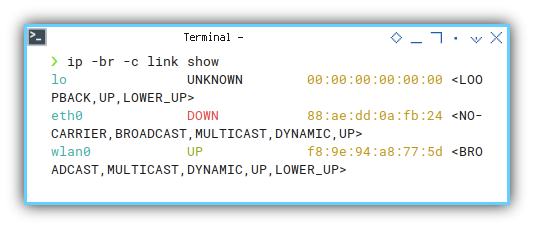
IP Address
Here is another alternative command, with filtering.
❯ ip addr show wlan03: wlan0: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,DYNAMIC,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc noqueue state UP group default qlen 1000
link/ether f8:9e:94:a8:77:5d brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 192.168.5.177/24 brd 192.168.5.255 scope global wlan0
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 fe80::fa9e:94ff:fea8:775d/64 scope link
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever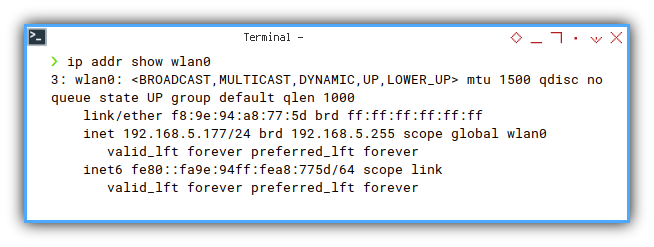
And also show the interface in brief, without detail.
❯ ip -br -c addr showlo UNKNOWN 127.0.0.1/8 ::1/128
eth0 DOWN
wlan0 UP 192.168.5.177/24 fe80::fa9e:94ff:fea8:775d/64 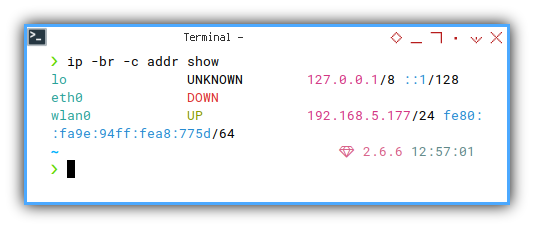
3: Other Tools
There are various useful tools, to examine wireless LAN.
RF Kill
My favorite is rfkill.
Although it is simple.
It is not always installed in by deafult in your distribution.
❯ rfkillID TYPE DEVICE SOFT HARD
0 bluetooth hci0 unblocked unblocked
1 wlan phy0 unblocked unblocked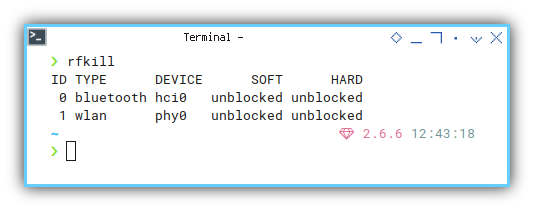
INXI
This is also my favorites,
since inxi show the relationship,
between device and driver.
❯ inxi -NazyNetwork:
Device-1: Intel Wi-Fi 6 AX201 160MHz driver: iwlwifi v: kernel
bus-ID: 00:14.3 chip-ID: 8086:4df0 class-ID: 0280
Device-2: Realtek RTL8111/8168/8411 PCI Express Gigabit Ethernet
vendor: Intel driver: r8169 v: kernel pcie: gen: 1 speed: 2.5 GT/s lanes: 1
port: 3000 bus-ID: 02:00.0 chip-ID: 10ec:8168 class-ID: 0200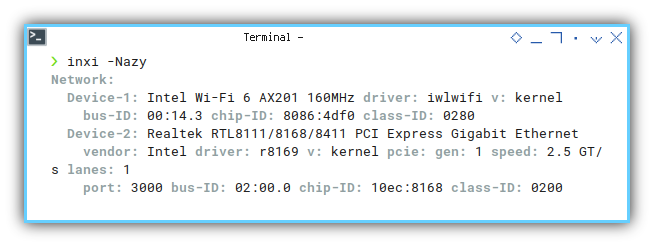
Just like lspci, here we can obtain below information:
- Device: Intel Wi-Fi 6 AX201
- Driver:
iwlwifi
Hardware Info
I can obtain the list interface easily here:
❯ sudo hwinfo --network --shortnetwork interface:
eth0 Ethernet network interface
lo Loopback network interface
wlan0 WLAN network interface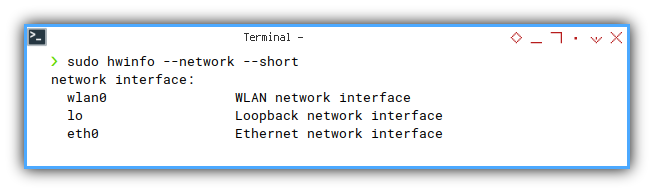
So that I can continue as below:
/sys/class
Memorize The Trick!
This is, my most important command.
❯ readlink /sys/class/net/wlan0/device/driver../../../bus/pci/drivers/iwlwifi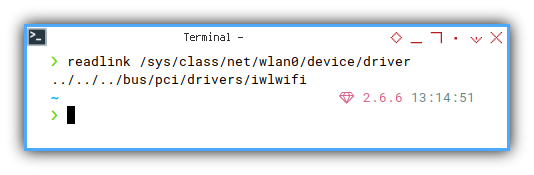
I can obtain below relationship:
- Interface: wlan0
- Driver:
iwlwifi
4: Driver: Modules
How do I know, if the modules loaded correctly, and stuff?
lsmod
lsmod print very long information.
Thus we have to filter manually with grep.
❯ lsmod | grep wifiiwlwifi 491520 1 iwlmvm
cfg80211 1118208 3 iwlmvm,iwlwifi,mac80211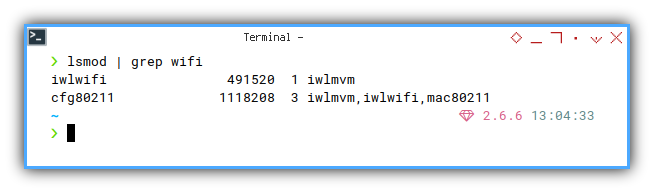
modprobe
I’m not sure why this has no output.
❯ sudo modprobe -v iwlwifi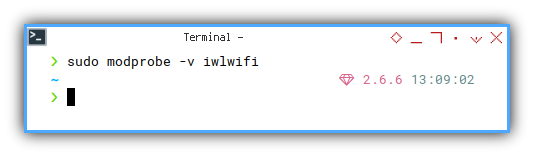
I guess still have to learn so much.
Driver Source Config
Just in case you are a curious one.
❯ ls /usr/src/linux/drivers/net/wireless/intel/iwlwifi
Kconfig❯ ls -l /usr/src/linux/drivers/net/wireless/intel/iwlwifi
total 8
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 5350 Dec 9 05:58 Kconfig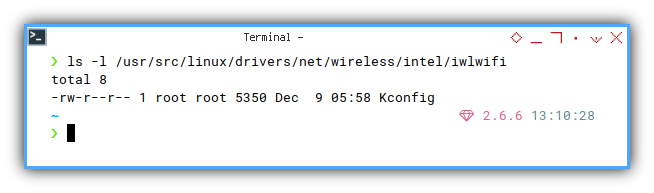
Driver Module Library
We need to know the place so we can debug, whenever there is a module issue.
❯ ls /usr/lib64/modules/6.0.12-artix1-1/kernel/drivers/net/wireless/intel/iwlwifi
dvm iwlwifi.ko.zst mvm❯ ls -l /usr/lib64/modules/6.0.12-artix1-1/kernel/drivers/net/wireless/intel/iwlwifi
total 304
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Dec 12 12:06 dvm
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 300570 Dec 9 05:58 iwlwifi.ko.zst
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Dec 12 12:06 mvm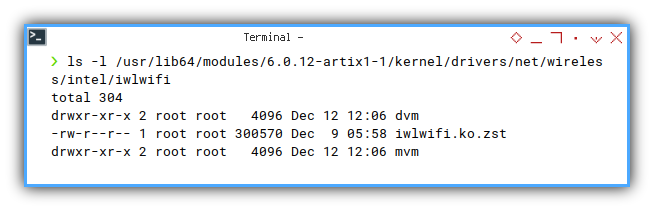
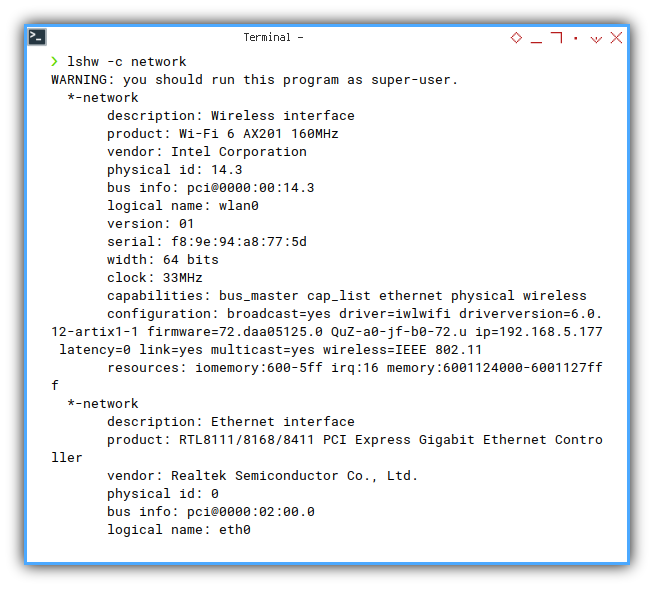
5: Device: Hardware List
This is actually just another tool.
❯ lshw -c networkWARNING: you should run this program as super-user.
*-network
description: Wireless interface
product: Wi-Fi 6 AX201 160MHz
vendor: Intel Corporation
physical id: 14.3
bus info: pci@0000:00:14.3
logical name: wlan0
version: 01
serial: f8:9e:94:a8:77:5d
width: 64 bits
clock: 33MHz
capabilities: bus_master cap_list ethernet physical wireless
configuration: broadcast=yes driver=iwlwifi driverversion=6.0.12-artix1-1 firmware=72.daa05125.0 QuZ-a0-jf-b0-72.u ip=192.168.5.177 latency=0 link=yes multicast=yes wireless=IEEE 802.11
resources: iomemory:600-5ff irq:16 memory:6001124000-6001127fff
*-network
description: Ethernet interface
product: RTL8111/8168/8411 PCI Express Gigabit Ethernet Controller
vendor: Realtek Semiconductor Co., Ltd.
physical id: 0
bus info: pci@0000:02:00.0
logical name: eth0
version: 15
serial: 88:ae:dd:0a:fb:24
capacity: 1Gbit/s
width: 64 bits
clock: 33MHz
capabilities: bus_master cap_list ethernet physical tp mii 10bt 10bt-fd 100bt 100bt-fd 1000bt-fd autonegotiation
configuration: autonegotiation=on broadcast=yes driver=r8169 driverversion=6.0.12-artix1-1 firmware=rtl8168h-2_0.0.2 02/26/15 latency=0 link=no multicast=yes port=twisted pair
resources: irq:19 ioport:3000(size=256) memory:80004000-80004fff memory:80000000-80003fff
WARNING: output may be incomplete or inaccurate, you should run this program as super-user.- .
You can print the output briefly.
❯ sudo lshw -class network -shortH/W path Device Class Description
===================================================================
/0/100/14.3 wlan0 network Wi-Fi 6 AX201 160MHz
/0/100/1c.7/0 eth0 network RTL8111/8168/8411 PCI Express Gigabit Ethernet Control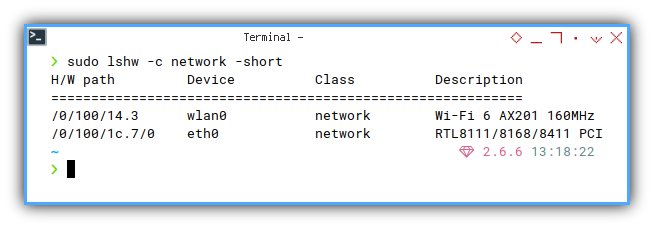
6: Diagnostic Messages
dmesg is very useful for troubleshooting.
Driver Event: iwlwifi
❯ sudo dmesg | grep iwl | head[ 3.860139] iwlwifi 0000:00:14.3: enabling device (0000 -> 0002)
[ 3.924579] iwlwifi 0000:00:14.3: api flags index 2 larger than supported by driver
[ 3.924601] iwlwifi 0000:00:14.3: TLV_FW_FSEQ_VERSION: FSEQ Version: 89.3.35.37
[ 3.925232] iwlwifi 0000:00:14.3: loaded firmware version 72.daa05125.0 QuZ-a0-jf-b0-72.ucode op_mode iwlmvm
[ 4.353346] iwlwifi 0000:00:14.3: Detected Intel(R) Wireless-AC 9462, REV=0x351
[ 4.507403] iwlwifi 0000:00:14.3: base HW address: f8:9e:94:a8:77:5d
[ 473.589032] iwlwifi 0000:00:14.3: No beacon heard and the session protection is over already...
[ 475.057386] iwlwifi 0000:00:14.3: No beacon heard and the session protection is over already...
[ 476.545206] iwlwifi 0000:00:14.3: No beacon heard and the session protection is over already...
[ 478.051093] iwlwifi 0000:00:14.3: No beacon heard and the session protection is over already...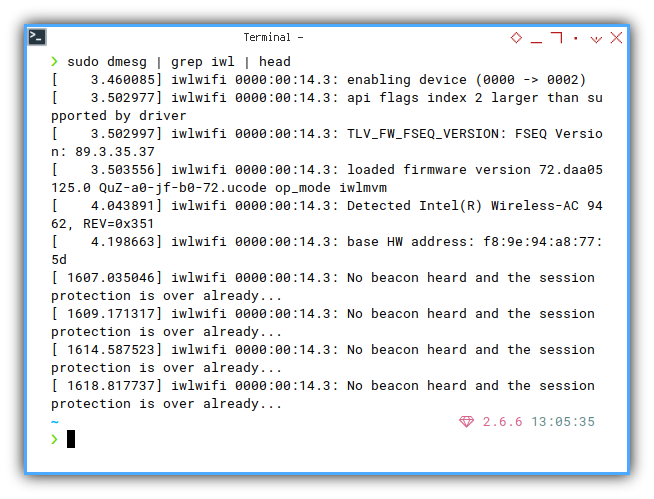
Interface Event: wlan0
❯ sudo dmesg | grep wlan0 | head[ 5.866504] wlan0: authenticate with 00:1e:42:25:4b:8d
[ 5.886650] wlan0: bad VHT capabilities, disabling VHT
[ 5.886656] wlan0: 80 MHz not supported, disabling VHT
[ 5.889612] wlan0: send auth to 00:1e:42:25:4b:8d (try 1/3)
[ 5.916525] wlan0: authenticated
[ 5.939950] wlan0: associate with 00:1e:42:25:4b:8d (try 1/3)
[ 5.945495] wlan0: RX AssocResp from 00:1e:42:25:4b:8d (capab=0x431 status=0 aid=3)
[ 5.950559] wlan0: associated
[ 6.044117] IPv6: ADDRCONF(NETDEV_CHANGE): wlan0: link becomes ready
[ 464.704046] wlan0: Connection to AP 00:1e:42:25:4b:8d lost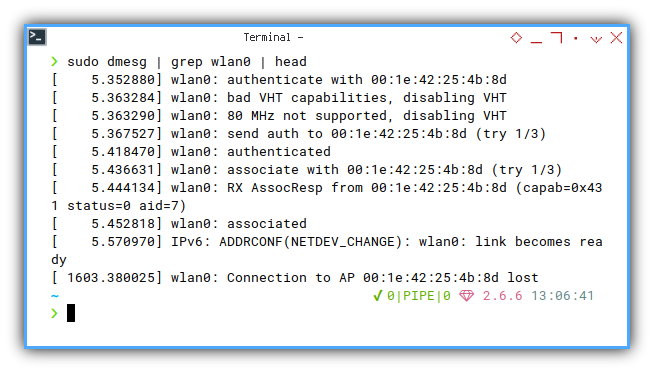
Firmware Event: All
❯ sudo dmesg | grep firmware[ 3.925232] iwlwifi 0000:00:14.3: loaded firmware version 72.daa05125.0 QuZ-a0-jf-b0-72.ucode op_mode iwlmvm
[ 4.210545] Bluetooth: hci0: Minimum firmware build 1 week 10 2014
[ 4.252576] Bluetooth: hci0: Found device firmware: intel/ibt-19-0-0.sfi
[ 4.265666] i915 0000:00:02.0: [drm] Finished loading DMC firmware i915/icl_dmc_ver1_09.bin (v1.9)
[ 5.902499] Bluetooth: hci0: Waiting for firmware download to complete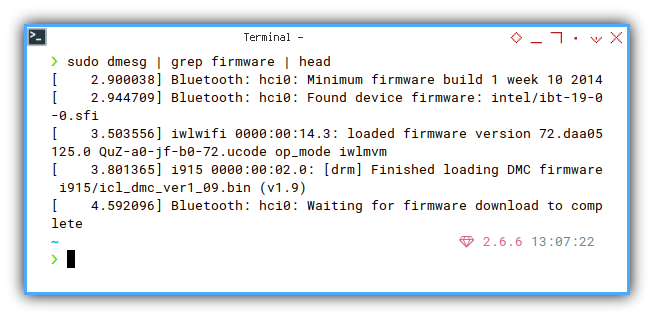
This way, we can debug, whether driver loaded or not.
7: Connection Manager
Depend on Your Distribution
Finally, the connection manager.
I’m using Artix with OpenRC that using connman instead of nmcli.
Connman Control
We can scan, and then dump the output
❯ connmanctl scan wifi
Scan completed for wifi
❯ connmanctl services
*AO RUT955_4B8D wifi_f89e94a8775d_5255543935355f34423844_managed_psk
wifi_f89e94a8775d_hidden_managed_psk
Japrut_Slebew wifi_f89e94a8775d_4a61707275745f536c65626577_managed_psk
DIR-612-4693 wifi_f89e94a8775d_4449522d3631322d34363933_managed_psk
DIRECT-3B-EPSON-L5190 Series wifi_f89e94a8775d_4449524543542d33422d4550534f4e2d4c3531393020536572696573_managed_psk
RUT950_5BBC wifi_f89e94a8775d_5255543935305f35424243_managed_psk
Production wifi_f89e94a8775d_50726f64756374696f6e_managed_psk
Soadamara110 wifi_f89e94a8775d_536f6164616d617261313130_managed_psk
TELTONIKA wifi_f89e94a8775d_54454c544f4e494b41_managed_psk
TELTONIKA_5G wifi_f89e94a8775d_54454c544f4e494b415f3547_managed_psk
TARIDA PORK FINEST wifi_f89e94a8775d_54415249444120504f524b2046494e455354_managed_psk
RUNNER_2.4G wifi_f89e94a8775d_52554e4e45525f322e3447_managed_psk
RUNNER_5G wifi_f89e94a8775d_52554e4e45525f3547_managed_psk
michael wifi_f89e94a8775d_6d69636861656c_managed_psk- .
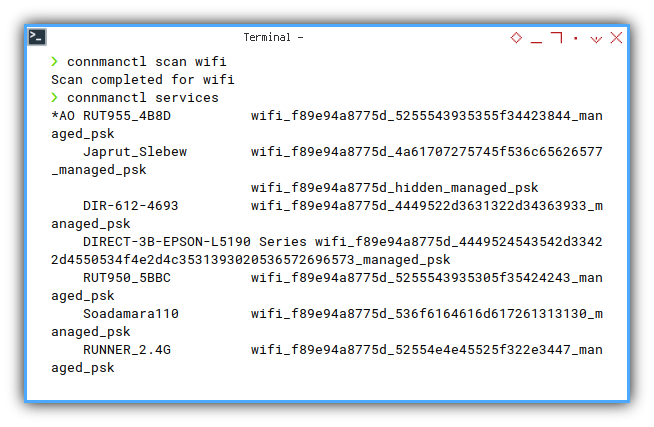
Or filter it later.
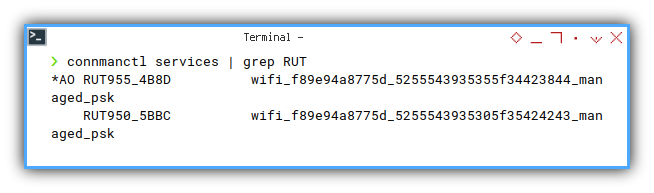
❯ connmanctl services | grep RUT
*AO RUT955_4B8D wifi_f89e94a8775d_5255543935355f34423844_managed_psk
RUT950_5BBC wifi_f89e94a8775d_5255543935305f35424243_managed_psk- .
Daemon
Sometimes, the wireless has unksnown trouble.
We can just restart, the daemon.
❯ sudo rc-service connmand restartnetmount | * Unmounting network filesystems ...
smb | * smb -> stop: smbd ... [ ok ]
smb | * smb -> stop: nmbd ... [ ok ]
connmand | * Stopping connmand ... [ ok ]
connmand | * Starting connmand ... [ ok ]
netmount | * Mounting network filesystems ...
smb | * smb -> start: smbd ... 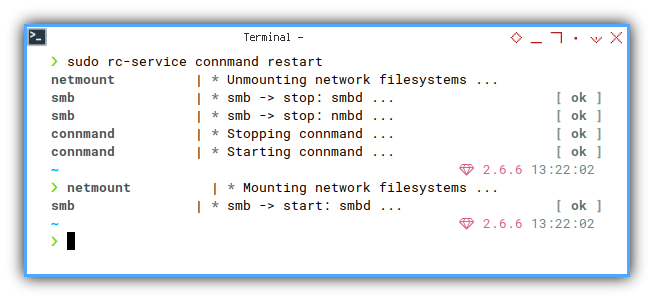
Other system
Create you own notes:
This article only cover Artix in my Mini PC.
Other system might use different tools,
such as iwctl while installing arch linux:
❯ sudo systemctl --now enable iwdSo don’t rely on my notes. Issue might be different on different system. And also, I might be wrong.
What is Next 🤔?
At least I know what’s inside my mini PC.
And I finally solve my own notebook issue. There is another article series about my Lenovo.
Consider continue reading [ Wireless: Device, Driver, Interface ].
Thank you for reading and visiting.