Preface
Goal: Examine wireless in system: device, driver, and interface.
I need to know my own system. So I write them down.
Table of Content
-
3: Other Tools
An Issue Behind This Article
Start from Working Machine as an Example
I have tried install arch linux in my Lenovo notebook last year But the thing is, the driver is not supported by linux kernel 5.x series. I guess I have to wait for arch linux to support linux kernel 6.x series. After a few months months, I finally installed arch with the right driver supported in my Lenovo.
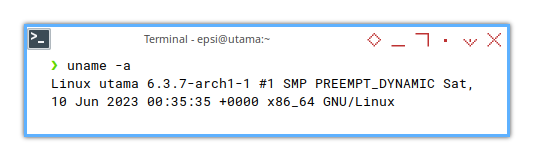
❯ uname -aLinux utama 6.3.7-arch1-1 #1 SMP PREEMPT_DYNAMIC Sat, 10 Jun 2023 00:35:35 +0000 x86_64 GNU/LinuxI intent to continue to install Gentoo. So I as a ritual, I prepare by writing every system related stuff, for my Lenovo.
I also found out that some of my linux knowledge is already obsolete. So I think writing these stuff is a must. I would like to rewrite some of my old article, such as wireles, audio, and othe linux subsystem. But this time for my Lenovo notebook.
1: Device: PCI and USB
There are a some common command in linux,
such as lsblk, lsmod, lspci, lsusb.
Devices can be found in either lsusb or lspci.
USB Devices
Vanilla arch user should install usbutils package.
# pacman -S usbutilsThen we can run the command
❯ lsusbBus 004 Device 001: ID 1d6b:0003 Linux Foundation 3.0 root hub
Bus 003 Device 004: ID 048d:c976 Integrated Technology Express, Inc. ITE Device(8176)
Bus 003 Device 003: ID 174f:244c Syntek Integrated Camera
Bus 003 Device 005: ID 0bda:4853 Realtek Semiconductor Corp. Bluetooth Radio
Bus 003 Device 002: ID 1a81:2232 Holtek Semiconductor, Inc. Lenovo Gaming Mouse
Bus 003 Device 001: ID 1d6b:0002 Linux Foundation 2.0 root hub
Bus 002 Device 001: ID 1d6b:0003 Linux Foundation 3.0 root hub
Bus 001 Device 001: ID 1d6b:0002 Linux Foundation 2.0 root hub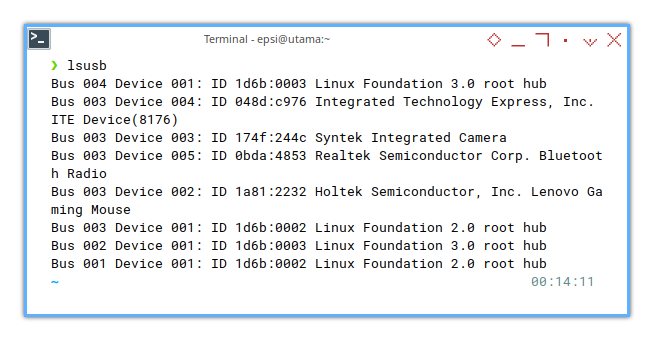
PCI Devices
❯ lspci0000:00:00.0 Host bridge: Intel Corporation Device 4649 (rev 02)
0000:00:01.0 PCI bridge: Intel Corporation 12th Gen Core Processor PCI Express x16 Controller #1 (rev 02)
0000:00:02.0 VGA compatible controller: Intel Corporation Alder Lake-P GT1 [UHD Graphics] (rev 0c)
0000:00:04.0 Signal processing controller: Intel Corporation Alder Lake Innovation Platform Framework Processor Participant (rev 02)
0000:00:06.0 System peripheral: Intel Corporation RST VMD Managed Controller
0000:00:07.0 PCI bridge: Intel Corporation Alder Lake-P Thunderbolt 4 PCI Express Root Port #0 (rev 02)
0000:00:08.0 System peripheral: Intel Corporation 12th Gen Core Processor Gaussian & Neural Accelerator (rev 02)
0000:00:0d.0 USB controller: Intel Corporation Alder Lake-P Thunderbolt 4 USB Controller (rev 02)
0000:00:0d.2 USB controller: Intel Corporation Alder Lake-P Thunderbolt 4 NHI #0 (rev 02)
0000:00:0e.0 RAID bus controller: Intel Corporation Volume Management Device NVMe RAID Controller
0000:00:14.0 USB controller: Intel Corporation Alder Lake PCH USB 3.2 xHCI Host Controller (rev 01)
0000:00:14.2 RAM memory: Intel Corporation Alder Lake PCH Shared SRAM (rev 01)
0000:00:15.0 Serial bus controller: Intel Corporation Alder Lake PCH Serial IO I2C Controller #0 (rev 01)
0000:00:16.0 Communication controller: Intel Corporation Alder Lake PCH HECI Controller (rev 01)
0000:00:1c.0 PCI bridge: Intel Corporation Device 51ba (rev 01)
0000:00:1c.3 PCI bridge: Intel Corporation Device 51bb (rev 01)
0000:00:1f.0 ISA bridge: Intel Corporation Alder Lake PCH eSPI Controller (rev 01)
0000:00:1f.3 Multimedia audio controller: Intel Corporation Alder Lake PCH-P High Definition Audio Controller (rev 01)
0000:00:1f.4 SMBus: Intel Corporation Alder Lake PCH-P SMBus Host Controller (rev 01)
0000:00:1f.5 Serial bus controller: Intel Corporation Alder Lake-P PCH SPI Controller (rev 01)
0000:01:00.0 VGA compatible controller: NVIDIA Corporation GA107M [GeForce RTX 3050 Ti Mobile] (rev a1)
0000:01:00.1 Audio device: NVIDIA Corporation Device 2291 (rev a1)
0000:2e:00.0 Ethernet controller: Realtek Semiconductor Co., Ltd. RTL8111/8168/8411 PCI Express Gigabit Ethernet Controller (rev 15)
0000:2f:00.0 Network controller: Realtek Semiconductor Co., Ltd. Device b852
10000:e0:06.0 PCI bridge: Intel Corporation 12th Gen Core Processor PCI Express x4 Controller #0 (rev 02)
10000:e1:00.0 Non-Volatile memory controller: Micron Technology Inc Device 5411 (rev 01)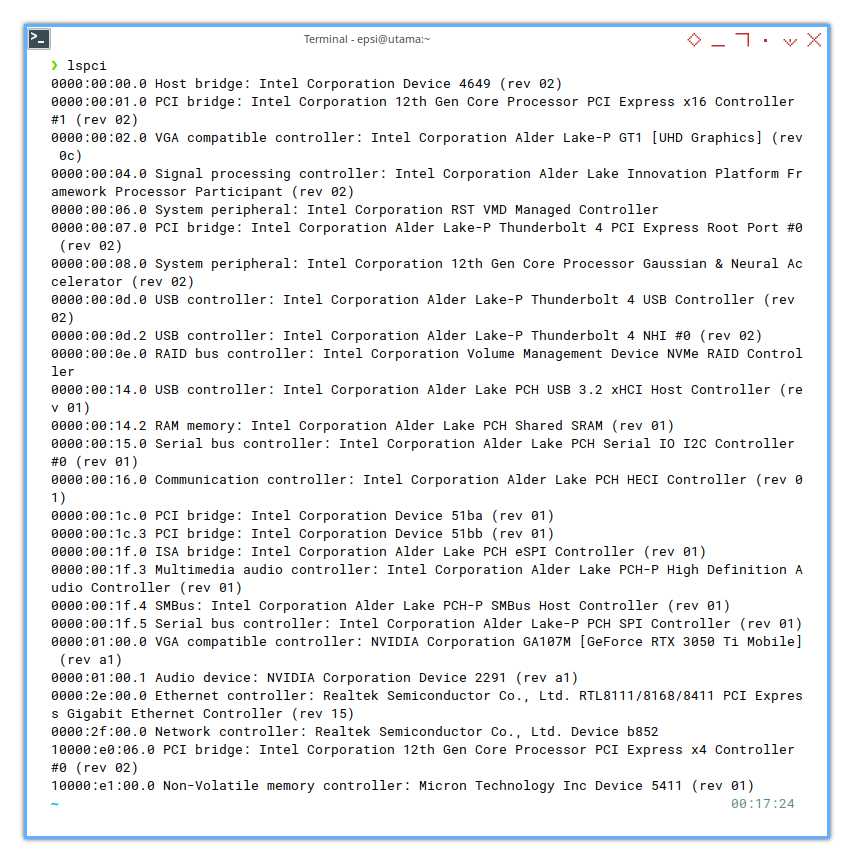
PCI Details
We can filter our query using grep.
❯ lspci | grep Network0000:2f:00.0 Network controller: Realtek Semiconductor Co., Ltd. Device b852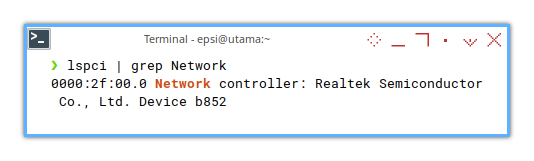
And then find the detail using the slot ID (bus:device.function).
❯ lspci -v -s 00:2f:000000:2f:00.0 Network controller: Realtek Semiconductor Co., Ltd. Device b852
Subsystem: Lenovo Device 4853
Flags: bus master, fast devsel, latency 0, IRQ 179, IOMMU group 17
I/O ports at 3000 [size=256]
Memory at 60200000 (64-bit, non-prefetchable) [size=1M]
Capabilities: <access denied>
Kernel driver in use: rtw89_8852be
Kernel modules: rtw89_8852be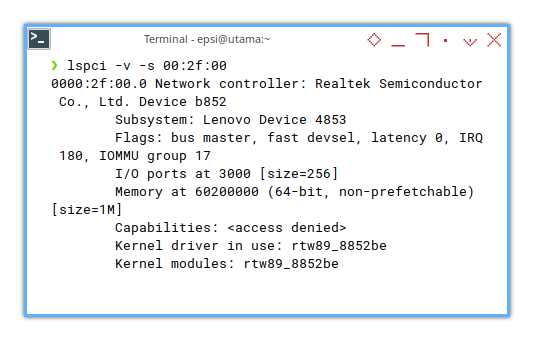
And find the kernel driver.
❯ lspci -k -s 00:2f:000000:2f:00.0 Network controller: Realtek Semiconductor Co., Ltd. Device b852
Subsystem: Lenovo Device 4853
Kernel driver in use: rtw89_8852be
Kernel modules: rtw89_8852be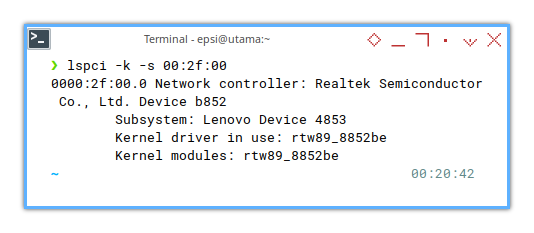
So here we have:
- Device: Realtek Semiconductor
- Driver:
rtw89_8852be
2: Interface: IP
ifconfig (obsolete)
Vanilla arch user should install net-tools package.
# pacman -S net-toolsVeteran (but dumb) like me,
might familiar with this obsolete ifconfig command.
❯ ifconfig wlan0wlan0: flags=4163<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,MULTICAST> mtu 1500
inet 192.168.0.237 netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast 192.168.0.255
inet6 fe80::f37d:d4d1:d542:abde prefixlen 64 scopeid 0x20<link>
ether 9c:2f:9d:9a:6d:e3 txqueuelen 1000 (Ethernet)
RX packets 11893 bytes 13493978 (12.8 MiB)
RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0
TX packets 5883 bytes 814933 (795.8 KiB)
TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0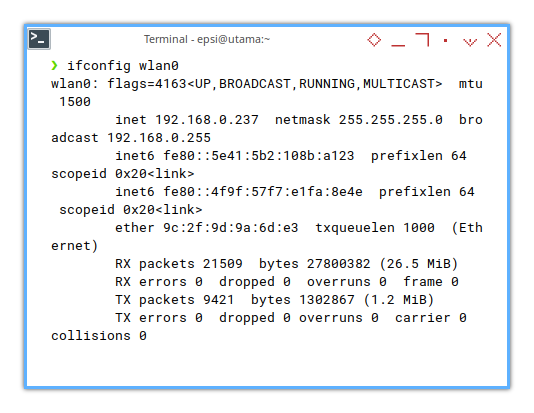
IP Link
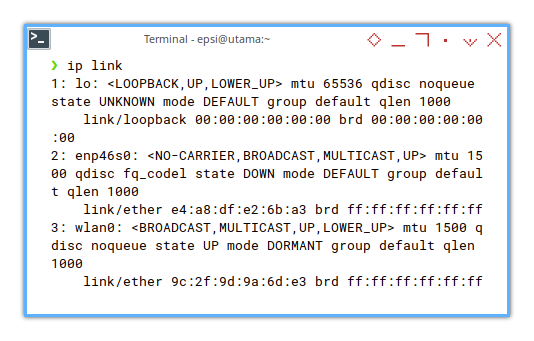
The basic command is so simple as below:
❯ ip link1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN mode DEFAULT group default qlen 1000
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
2: enp46s0: <NO-CARRIER,BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP> mtu 1500 qdisc fq_codel state DOWN mode DEFAULT group default qlen 1000
link/ether e4:a8:df:e2:6b:a3 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
3: wlan0: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc noqueue state UP mode DORMANT group default qlen 1000
link/ether 9c:2f:9d:9a:6d:e3 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ffAs we find wlan0 interface, we can then filter the result:
❯ ip link show wlan03: wlan0: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc noqueue state UP mode DORMANT group default qlen 1000
link/ether 9c:2f:9d:9a:6d:e3 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff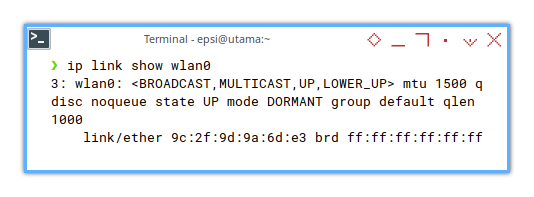
Or even show in brief, without detail.
❯ ip -br -c link showlo UNKNOWN 00:00:00:00:00:00 <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP>
enp46s0 DOWN e4:a8:df:e2:6b:a3 <NO-CARRIER,BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP>
wlan0 UP 9c:2f:9d:9a:6d:e3 <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP>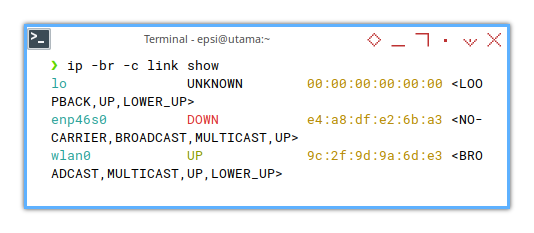
IP Address
Here is another alternative command, with filtering.
❯ ip addr show wlan03: wlan0: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc noqueue state UP group default qlen 1000
link/ether 9c:2f:9d:9a:6d:e3 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 192.168.0.237/24 brd 192.168.0.255 scope global dynamic noprefixroute wlan0
valid_lft 6380sec preferred_lft 6380sec
inet6 fe80::f37d:d4d1:d542:abde/64 scope link noprefixroute
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever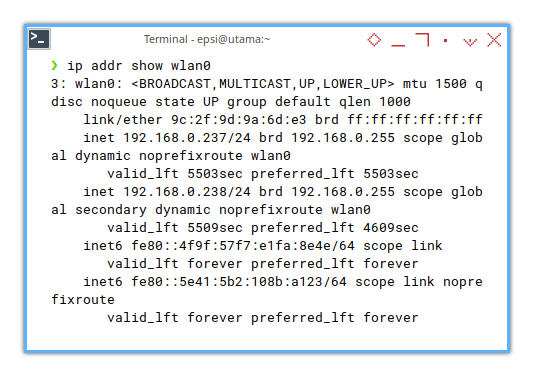
And also show the interface in brief, without detail.
❯ ip -br -c addr showlo UNKNOWN 127.0.0.1/8 ::1/128
enp46s0 DOWN
wlan0 UP 192.168.0.237/24 fe80::f37d:d4d1:d542:abde/64 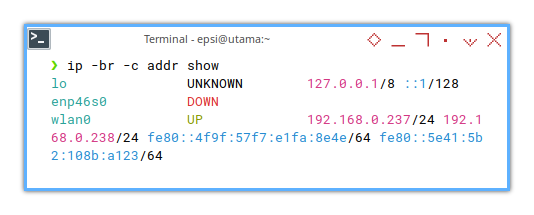
3: Other Tools
There are various useful tools, to examine wireless LAN.
RF Kill
My favorite is rfkill.
Although it is simple.
It is not always installed in by deafult in your distribution.
❯ rfkillID TYPE DEVICE SOFT HARD
0 wlan ideapad_wlan unblocked unblocked
1 bluetooth ideapad_bluetooth unblocked unblocked
2 bluetooth hci0 unblocked unblocked
3 wlan phy0 unblocked unblocked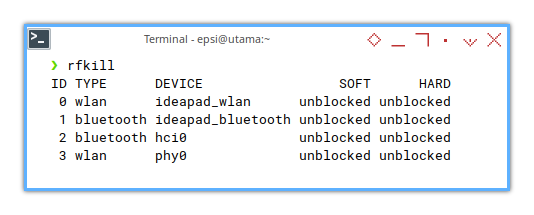
INXI
Vanilla arch user should install inxi package.
# pacman -S inxiThis is also my favorites,
since inxi show the relationship,
between device and driver.
❯ inxi -NazyNetwork:
Network:
Device-1: Realtek RTL8111/8168/8411 PCI Express Gigabit Ethernet
vendor: Lenovo driver: r8169 v: kernel port: 4000 bus-ID: 0000:2e:00.0
chip-ID: 10ec:8168 class-ID: 0200
Device-2: Realtek vendor: Lenovo driver: rtw89_8852be v: kernel port: 3000
bus-ID: 0000:2f:00.0 chip-ID: 10ec:b852 class-ID: 0280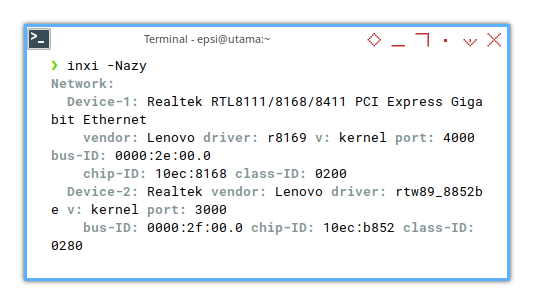 :
:
Just like lspci, here we can obtain below information:
- Device: Realtek
- Driver:
rtw89_8852be
Hardware Info
I can obtain the list interface easily here:
❯ sudo hwinfo --network --short
[sudo] password for epsi: network interface:
lo Loopback network interface
wlan0 WLAN network interface
enp46s0 Ethernet network interface
So that I can continue as below:
/sys/class
Memorize The Trick!
This is still, my most important command.
❯ readlink /sys/class/net/wlan0/device/driver../../../../bus/pci/drivers/rtw89_8852be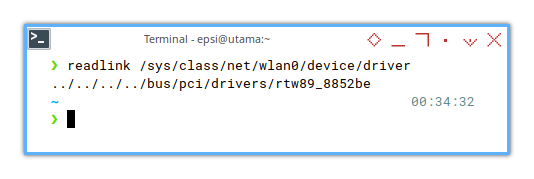
I can obtain below relationship:
- Interface: wlan0
- Driver:
rtw89_8852be
4: Driver: Modules
How do I know, if the modules loaded correctly, and stuff?
lsmod
lsmod print very long information.
Thus we have to filter manually with grep.
❯ lsmod | grep rtwrtw89_8852be 16384 0
rtw89_8852b 356352 1 rtw89_8852be
rtw89_pci 86016 1 rtw89_8852be
rtw89_core 602112 2 rtw89_8852b,rtw89_pci
mac80211 1503232 2 rtw89_core,rtw89_pci
cfg80211 1286144 3 rtw89_8852b,rtw89_core,mac80211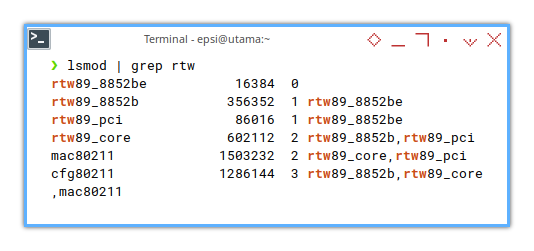
modprobe
I’m not sure why this has no output.
❯ sudo modprobe -v rtw89_8852beNothing happened.
I guess still have to learn so much.
Driver Source Config
Just in case you are a curious one.
❯ ls /usr/src/Show empty folder.
Driver Module Library
We need to know the place so we can debug, whenever there is a module issue.
❯ ls /usr/lib64/modules/6.3.5-arch1-1/kernel/drivers/net/wireless/realtek/rtw89/rtw89_8852ae.ko.zst rtw89_8852be.ko.zst rtw89_8852ce.ko.zst rtw89_core.ko.zst
rtw89_8852a.ko.zst rtw89_8852b.ko.zst rtw89_8852c.ko.zst rtw89_pci.ko.zst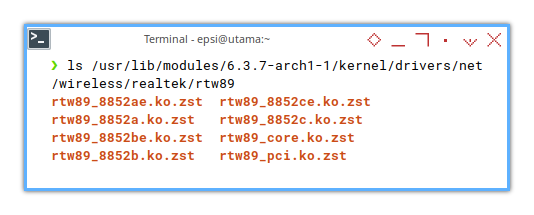
5: Device: Hardware List
Vanilla arch user should install lshw package.
# pacman -S lshwThis is actually just another tool.
❯ lshw -c networkWARNING: you should run this program as super-user.
*-network
description: Ethernet interface
product: RTL8111/8168/8411 PCI Express Gigabit Ethernet Controller
vendor: Realtek Semiconductor Co., Ltd.
physical id: 0
bus info: pci@0000:2e:00.0
logical name: enp46s0
version: 15
serial: e4:a8:df:e2:6b:a3
capacity: 1Gbit/s
width: 64 bits
clock: 33MHz
capabilities: bus_master cap_list ethernet physical tp mii 10bt 10bt-fd 100bt 100bt-fd 1000bt-fd autonegotiation
configuration: autonegotiation=on broadcast=yes driver=r8169 driverversion=6.3.5-arch1-1 firmware=rtl8168h-2_0.0.2 02/26/15 latency=0 link=no multicast=yes port=twisted pair
resources: irq:18 ioport:4000(size=256) memory:60304000-60304fff memory:60300000-60303fff
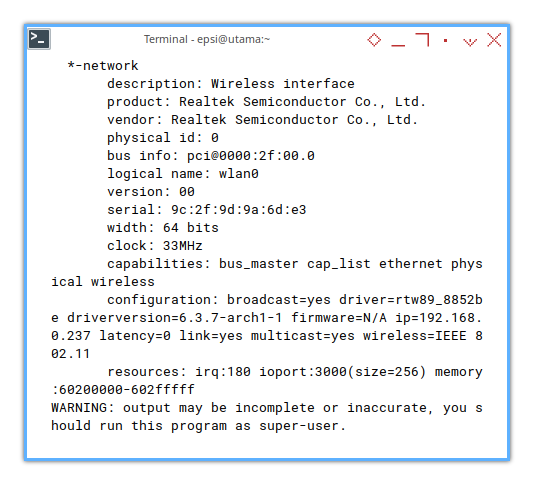
*-network
description: Wireless interface
product: Realtek Semiconductor Co., Ltd.
vendor: Realtek Semiconductor Co., Ltd.
physical id: 0
bus info: pci@0000:2f:00.0
logical name: wlan0
version: 00
serial: 9c:2f:9d:9a:6d:e3
width: 64 bits
clock: 33MHz
capabilities: bus_master cap_list ethernet physical wireless
configuration: broadcast=yes driver=rtw89_8852be driverversion=6.3.5-arch1-1 firmware=N/A ip=192.168.0.237 latency=0 link=yes multicast=yes wireless=IEEE 802.11
resources: irq:179 ioport:3000(size=256) memory:60200000-602fffff
WARNING: output may be incomplete or inaccurate, you should run this program as super-user.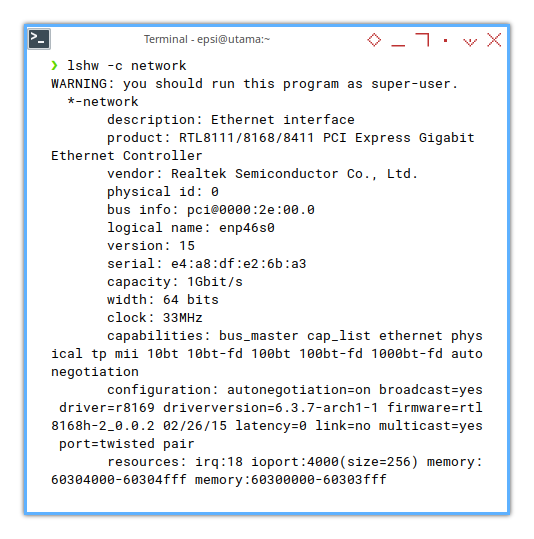
You can print the output briefly.
❯ sudo lshw -class network -shortH/W path Device Class Description
=========================================================
/0/100/1c/0 enp46s0 network RTL8111/8168/8411 PCI Express Gigabit Ethernet Controller
/0/100/1c.3/0 wlan0 network Realtek Semiconductor Co., Ltd.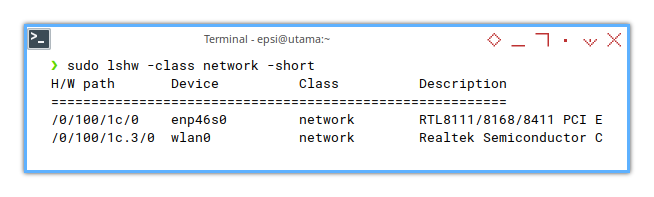
6: Diagnostic Messages
dmesg is very useful for troubleshooting.
Driver Event: iwlwifi
❯ sudo dmesg | grep "rtw89_8852be 0000:2f:00.0" | head[ 18.204773] rtw89_8852be 0000:2f:00.0: enabling device (0000 -> 0003)
[ 18.206961] rtw89_8852be 0000:2f:00.0: Firmware version 0.27.32.1, cmd version 0, type 1
[ 18.206964] rtw89_8852be 0000:2f:00.0: Firmware version 0.27.32.1, cmd version 0, type 3
[ 18.490432] rtw89_8852be 0000:2f:00.0: chip rfe_type is 1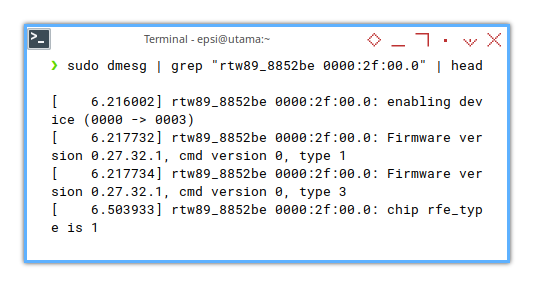
Interface Event: wlan0
❯ sudo dmesg | grep wlan0 | head[ 24.145322] wlan0: authenticate with 9c:a2:f4:c1:da:69
[ 24.359534] wlan0: send auth to 9c:a2:f4:c1:da:69 (try 1/3)
[ 24.365653] wlan0: authenticated
[ 24.369133] wlan0: associate with 9c:a2:f4:c1:da:69 (try 1/3)
[ 24.385166] wlan0: RX AssocResp from 9c:a2:f4:c1:da:69 (capab=0x1011 status=0 aid=20)
[ 24.493913] wlan0: associated
[ 24.494116] wlan0: Limiting TX power to 30 (30 - 0) dBm as advertised by 9c:a2:f4:c1:da:69
[ 24.627369] IPv6: ADDRCONF(NETDEV_CHANGE): wlan0: link becomes ready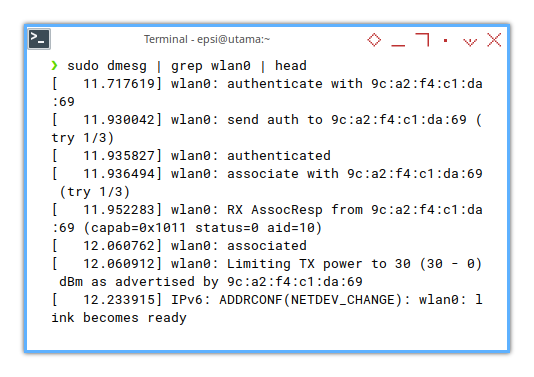
Firmware Event: All
❯ sudo dmesg | grep firmware[ 16.802173] systemd[1]: TPM2 PCR Machine ID Measurement was skipped because of an unmet condition check (ConditionPathExists=/sys/firmware/efi/efivars/StubPcrKernelImage-4a67b082-0a4c-41cf-b6c7-440b29bb8c4f).
[ 18.185262] i915 0000:00:02.0: [drm] Finished loading DMC firmware i915/adlp_dmc.bin (v2.19)
[ 18.226343] i915 0000:00:02.0: [drm] GT0: GuC firmware i915/adlp_guc_70.bin version 70.5.1
[ 18.226348] i915 0000:00:02.0: [drm] GT0: HuC firmware i915/tgl_huc.bin version 7.9.3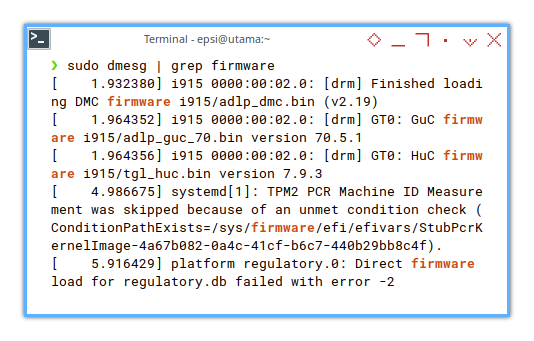
This way, we can debug, whether driver loaded or not.
What is Next 🤔?
I should know what’s inside my notebook. So I can be ready for Gentoo. There is still low level wireless to go.
Consider continue reading [ Wireless: Low Level Connection ].