Preface
Goal: Examine wireless in system: device, driver, and interface.
This is not a recommended way to connect to your wifi. But I write this anyway for the sake of curiousity.
For daily usage,
you should use either iwd, nmcli or connman instead,
Table of Content
Wireless Tools
This is lower level wireless tool.
ip and iw
In the context of wireless tools in Linux,
ip and iw are both command-line utilities
that are used for managing network interfaces,
but they serve different purposes.
While both ip and iw are useful networking tools in Linux,
ip is a general-purpose command for managing networking in general,
while iw is focused specifically on wireless network interfaces.
In real low level usage, we need both command.
Using iw
We need to list our device. Physical name could be different.
Since iwconfig has been deprecated since decades ago,
we are using iw.
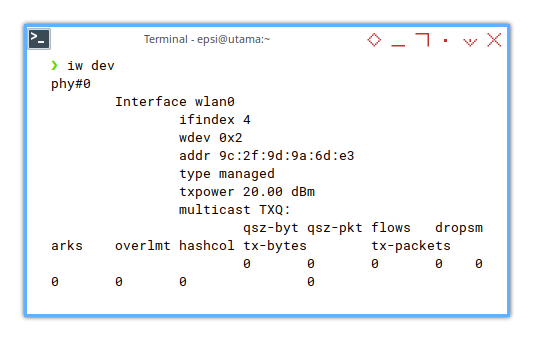
❯ iw dev This would looks like
When you are connected with an SSID, This would looks like below:
phy#0
Interface wlan0
ifindex 3
wdev 0x1
addr 9c:2f:9d:9a:6d:e3
ssid E.R. Nurwijayadi
type managed
channel 161 (5805 MHz), width: 80 MHz, center1: 5775 MHz
txpower 20.00 dBm
multicast TXQ:
qsz-byt qsz-pkt flows drops marks overlmt hashcol tx-bytes tx-packets
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0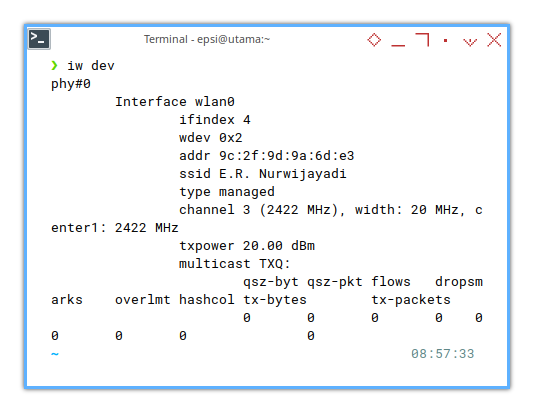
iw Issue
There is a case that iw return nothing.
❯ iw dev In order to use iw,
we need to start either iwd or wpa_supplicant.
❯ sudo systemctl start iwdOr
❯ sudo systemctl start wpa_supplicantI can’t replicate this issue. So I’m not sure about this.
Failed
❯ sudo iw dev wlan0 connect "E.R. Nurwijayadi"
command failed: Network is down (-100)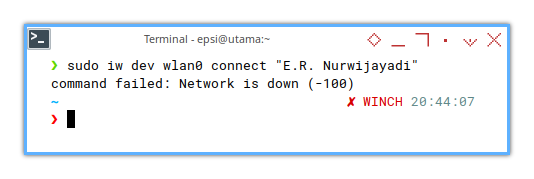
Powering Up
We need a little help from ip command.
❯ ip link show wlan0 3: wlan0: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc noqueue state UP mode DORMANT group default qlen 1000
link/ether 9c:2f:9d:9a:6d:e3 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff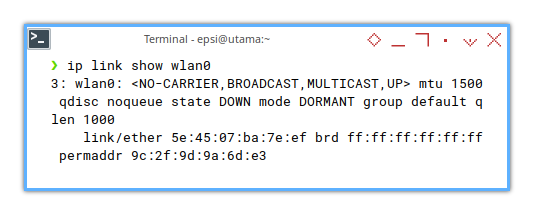
❯ sudo ip link set wlan0 up
[sudo] password for epsi: 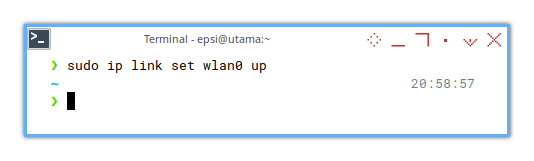
Scanning SSID
We can also scan our available SSID for our wireless.
❯ sudo iw dev wlan0 scan
command failed: Device or resource busy (-16)Let’s try again.
❯ sudo iw dev wlan0 scan | grep SSID SSID: TELTONIKA
* SSID List
SSID: TARIDA PORK FINEST
SSID: E.R. Nurwijayadi
SSID: Soadamara110
SSID: RUT955_4B8D
* SSID List
* UTF-8 SSID
SSID: TELTONIKA_5G
* SSID List
SSID: OPIS
SSID: DIRECT-3B-EPSON-L5190 Series
SSID: FreeNet
SSID: Bangtan
SSID: RUNNER_5G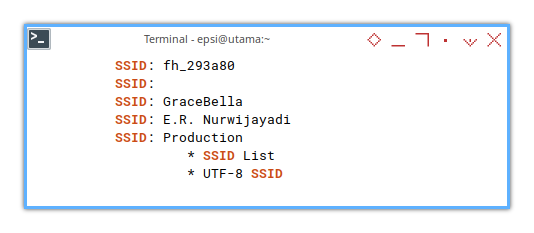
From this step, we may choose method to connect to your wireless.
There are many methods, but you can only chooses one method at a time.
This will show you NetworkManager using nmcli command.
Connecting
Oh man… low level is a mess.
But you can always try for the sake of knowledge.
Consider this iw dev command.
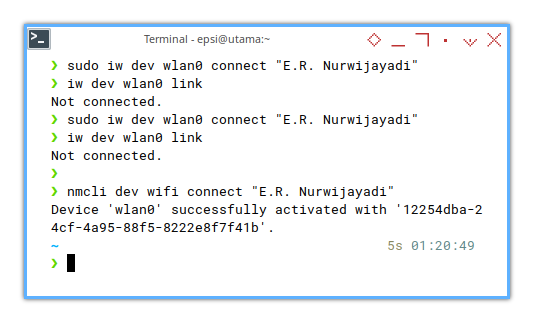
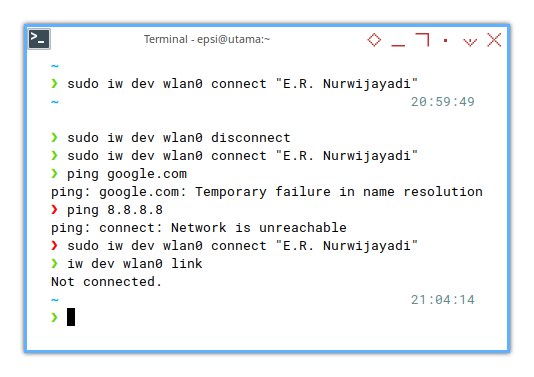
❯ sudo iw dev wlan0 connect "E.R. Nurwijayadi"
[sudo] password for epsi:
command failed: Operation already in progress (-114)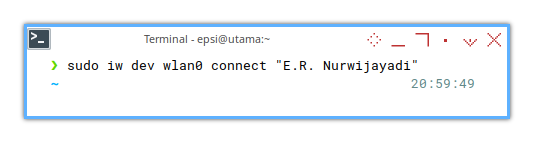
I guess I have to use nmcli instead.
We will explore this later.
And try again
Using ‘nmcli’
NetworkManager is very common.
I’m using Vanilla Arch with systemd that using nmcli.
Again, let’s do it with command line.
❯ nmcli dev wifi connect "E.R. Nurwijayadi"
Error: NetworkManager is not running.Of course we need to run Network manager first.
❯ sudo systemctl start NetworkManagerThen we can connect.
❯ nmcli dev wifi connect "E.R. Nurwijayadi"
Error: Connection activation failed: Secrets were required, but not provided.Allright we need to provide the password.
❯ nmcli dev wifi connect "E.R. Nurwijayadi" password oyenyebus
Device 'wlan0' successfully activated with '4525cdf8-a007-446e-b3c2-cd5172ce44df'.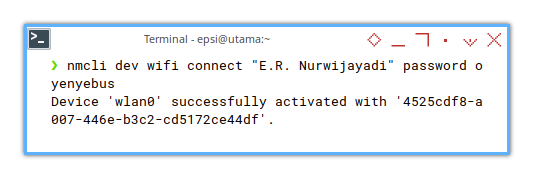
Other time I don’t even need to provide the password.
❯ nmcli dev wifi connect "E.R. Nurwijayadi"Device 'wlan0' successfully activated with '70f471c9-f896-424d-9ac6-25812c39994e'.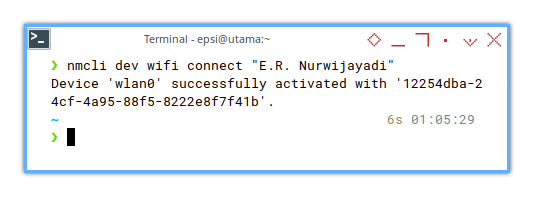
Note that the actual ID will remain the same.
Check Connection
Again.. check your connexion.
❯ iw dev wlan0 link Connected to 9c:a2:f4:c1:da:69 (on wlan0)
SSID: E.R. Nurwijayadi
freq: 5805
RX: 2728763 bytes (8007 packets)
TX: 153923 bytes (1026 packets)
signal: -33 dBm
rx bitrate: 1080.6 MBit/s 80MHz HE-MCS 10 HE-NSS 2 HE-GI 0 HE-DCM 0
tx bitrate: 1200.9 MBit/s 80MHz HE-MCS 11 HE-NSS 2 HE-GI 0 HE-DCM 0
bss flags: short-slot-time
dtim period: 1
beacon int: 100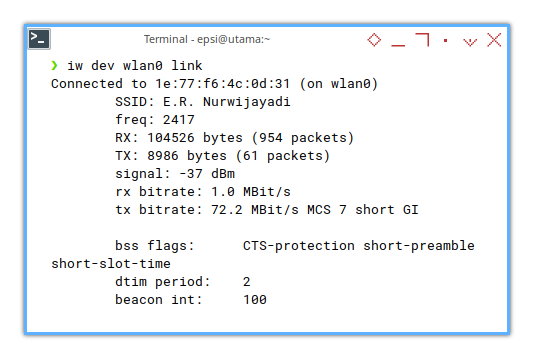
DHCP
We still have to reserve our IP with dhcpcd.
❯ dhclient wlan0
RTNETLINK answers: File existsNow you can ping
❯ ping google.com -c 2 PING forcesafesearch.google.com (216.239.38.120) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from any-in-2678.1e100.net (216.239.38.120): icmp_seq=1 ttl=114 time=20.8 ms
64 bytes from any-in-2678.1e100.net (216.239.38.120): icmp_seq=2 ttl=114 time=20.8 ms
--- forcesafesearch.google.com ping statistics ---
2 packets transmitted, 2 received, 0% packet loss, time 1002ms
rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 20.803/20.804/20.806/0.001 ms
Disconnect
Finally, you may disconnect,
❯ nmcli dev disconnect wlan0 Device 'wlan0' successfully disconnected.
What is Next 🤔?
I should know what’s inside my notebook.
So I can be ready for Gentoo.
After this mess,
we can get into proper connection
with either iwd, nmcli or connman
Consider continue reading [ Wireless: INet Wireless Daemon ].