Preface
Goal: Thorough /etc/samba/smb.conf example
Table of Content
-
Preface: Table of Content
Overview
This is more like a network topic rather than a multiboot topic, I gather this samba article here, because of my multiboot situation.
Samba Configuration
smb.conf for each distribution is available at:
1: Share Definitions
Common Share Definition: Debian, Fedora, openSUSE, KaOSx
The basic smb.conf is similar.
Because I copy paste from my Debian to other distribution.
I made it that way
[Samba]
path = /media/Works/Samba/
available = yes
valid users = epsi
read only = no
browseable = yes
public = yes
writeable = yes
# [homes]
# read only = yes
# create mask = 0700
# directory mask = 0700
# valid users = %SOther Share Definitions
Off course you can add more share definitions, but the default setting is difference between distribution. For example, fedora and openSUSE use printer path, as /var/tmp rather than /var/spool/samba.
# [homes]
# read only = yes
# create mask = 0700
# directory mask = 0700
# valid users = %S
[printers]
comment = All Printers
browseable = no
path = /var/spool/samba
printable = yes
guest ok = no
read only = yes
create mask = 0700
[print$]
comment = Printer Drivers
path = /var/lib/samba/printers
browseable = yes
read only = yes
guest ok = no2: Global Configuration
Fedora
I do not know why, but the default config is really short.
[global]
workgroup = WORKGROUP
security = user
passdb backend = tdbsamHave a look at the smb.conf config for Fedora:
I have an issue with SELinux in Fedora. The easiest workaround is simply to disable SELinux. However this quick-fix is considered bad practice.
Debian
Debian takes longer default cofig.
[global]
## Browsing/Identification ###
workgroup = WORKGROUP
dns proxy = no
#### Networking ####
#### Debugging/Accounting ####
log file = /var/log/samba/log.%m
max log size = 1000
syslog = 0
panic action = /usr/share/samba/panic-action %d
####### Authentication #######
server role = standalone server
passdb backend = tdbsam
obey pam restrictions = yes
unix password sync = yes
passwd program = /usr/bin/passwd %u
passwd chat = *Enter\snew\s*\spassword:* %n\n *Retype\snew\s*\spassword:* %n\n *password\supdated\ssuccessfully* .
pam password change = yes
map to guest = bad user
########## Domains ###########
############ Misc ############
usershare allow guests = yesHave a look at the smb.conf config for Debian:
KaOSx
Very similar with Debian.
Except that I have to put netbios name,
in order to work from local area network.
[global]
## Browsing/Identification ###
workgroup = WORKGROUP
dns proxy = no
netbios name = andalan
#### Networking ####
#### Debugging/Accounting ####
log file = /var/log/samba/log.%m
max log size = 1000
syslog = 0
panic action = /usr/share/samba/panic-action %d
####### Authentication #######
server role = standalone server
passdb backend = tdbsam
obey pam restrictions = yes
unix password sync = yes
passwd program = /usr/bin/passwd %u
passwd chat = *Enter\snew\s*\spassword:* %n\n *Retype\snew\s*\spassword:* %n\n *password\supdated\ssuccessfully* .
pam password change = yes
map to guest = bad user
########## Domains ###########
############ Misc ############
usershare allow guests = yesHave a look at the smb.conf config for KaOSx:
openSUSE
openSUSE has different beast of configuration.
I also have to put netbios name.
[global]
workgroup = WORKGROUP
passdb backend = tdbsam
printing = cups
printcap name = cups
printcap cache time = 750
cups options = raw
map to guest = Bad User
include = /etc/samba/dhcp.conf
logon path = \\%L\profiles\.msprofile
logon home = \\%L\%U\.9xprofile
logon drive = P:
usershare allow guests = No
add machine script = /usr/sbin/useradd -c Machine -d /var/lib/nobody -s /bin/false %m$
domain logons = No
domain master = No
ldap admin dn =
security = user
wins server =
wins support = No
netbios name = andalanHave a look at the smb.conf config for openSUSE:
3: Real Life Access
Preparation
For each linux, add samba Password.
$ sudo smbpasswd -a epsi
New SMB password:
Retype new SMB password:
Added user epsi.And check
$ sudo pdbedit -L
epsi:1000:Epsi SayidinaFedora
Check Service.
sudo systemctl status smb nmbCheck samba:
% smbtree
WORKGROUP
\\ANDALAN Samba 4.8.1
\\ANDALAN\IPC$ IPC Service (Samba 4.8.1)
\\ANDALAN\Samba 
% smbclient -L localhost
Enter WORKGROUP\epsi's password:
Sharename Type Comment
--------- ---- -------
Samba Disk
IPC$ IPC IPC Service (Samba 4.8.1)
Reconnecting with SMB1 for workgroup listing.
Server Comment
--------- -------
Workgroup Master
--------- -------
WORKGROUP 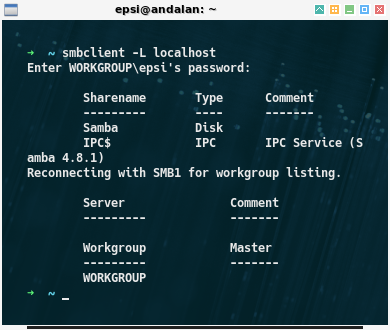
Access form Android:
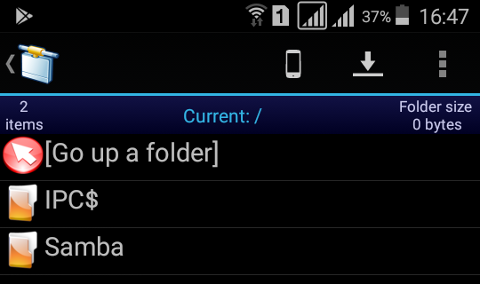
Debian
Check Service.
$ sudo systemctl status smbd nmbdCheck samba:
$ smbtree
WORKGROUP
\\ANDALAN Samba 4.7.7
\\ANDALAN\IPC$ IPC Service (Samba 4.7.7)
\\ANDALAN\Samba 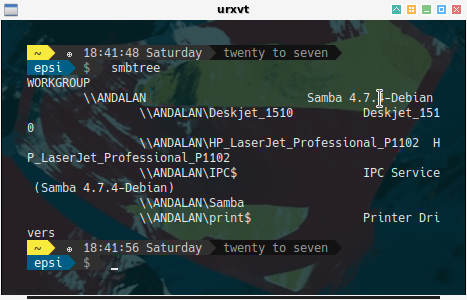
$ smbclient -L localhost
WARNING: The "syslog" option is deprecated
Enter WORKGROUP\epsi's password:
Sharename Type Comment
--------- ---- -------
print$ Disk Printer Drivers
Samba Disk
IPC$ IPC IPC Service (Samba 4.7.4-Debian)
HP_LaserJet_Professional_P1102 Printer HP_LaserJet_Professional_P1102
Deskjet_1510 Printer Deskjet_1510
Reconnecting with SMB1 for workgroup listing.
Server Comment
--------- -------
Workgroup Master
--------- -------
WORKGROUP 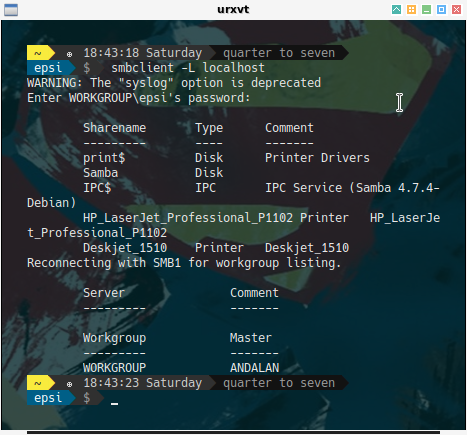
Access form Android:
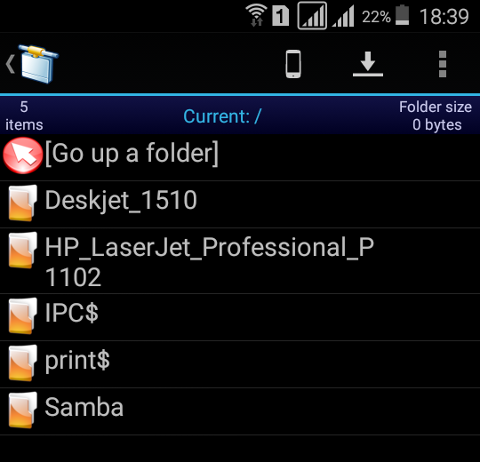
KaOSx
% sudo systemctl status smbd nmbdCheck samba:
% smbtree
WORKGROUP
\\ANDALAN Samba 4.7.7
\\ANDALAN\IPC$ IPC Service (Samba 4.7.7)
\\ANDALAN\Samba 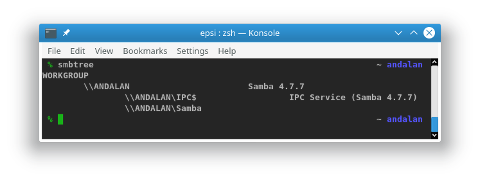
% smbclient -L localhost
WARNING: The "syslog" option is deprecated
Enter WORKGROUP\epsi's password:
Sharename Type Comment
--------- ---- -------
Samba Disk
IPC$ IPC IPC Service (Samba 4.7.7)
Reconnecting with SMB1 for workgroup listing.
Server Comment
--------- -------
Workgroup Master
--------- -------
WORKGROUP ANDALAN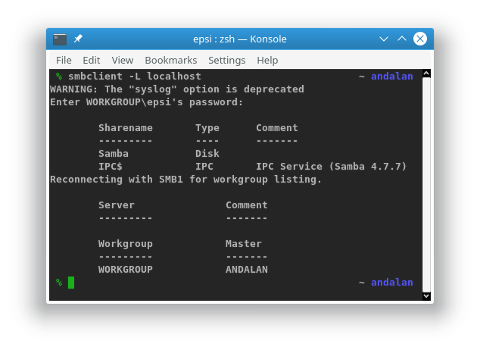
openSUSE
sudo systemctl status smb nmbCheck samba:
% smbtree
WORKGROUP
\\ANDALAN Samba 4.6.13-git.72.2a684235f4112.1-SUSE-SLE_12-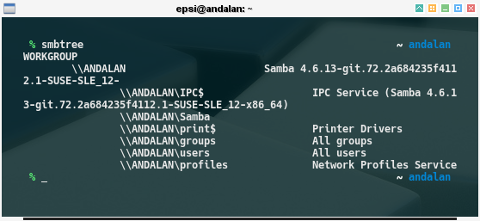
% smbclient -L localhost
Enter WORKGROUP\epsi's password:
Domain=[ANDALAN] OS=[Windows 6.1] Server=[Samba 4.6.13-git.72.2a684235f4112.1-SUSE-SLE_12-x86_64]
Sharename Type Comment
--------- ---- -------
profiles Disk Network Profiles Service
users Disk All users
groups Disk All groups
print$ Disk Printer Drivers
Samba Disk
IPC$ IPC IPC Service (Samba 4.6.13-git.72.2a684235f4112.1-SUSE-SLE_12-x86_64)
epsi Disk Home Directories
Domain=[ANDALAN] OS=[Windows 6.1] Server=[Samba 4.6.13-git.72.2a684235f4112.1-SUSE-SLE_12-x86_64]
Server Comment
--------- -------
Workgroup Master
--------- -------
WORKGROUP ANDALAN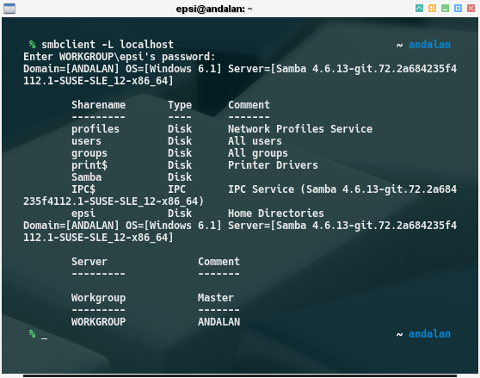
Access form Android:
Conclusion
Finished. We are done with multiboot article series. Consider going back reading old article [ Multiboot: Setting up Partition ].