The Document
This article contain all article slides. Slide by slide, so anyone can copy desired slide, without the need to open the Impress slide, or the PDF version.
I believe, a ready to use slide, is useful to help people in the group discussion.
Original Presentation
I usually draft a presentation in a simple text based, that I can write down in any text editor.
Then I show in web based for a few moment (actually months). This give time to append any additional material freely, create necessary figure, and also correct any typo, or even dead links.
You can watch the presentation here:
This text based presentation is the most authentic version, with all the links required provided.
Impress
This presentation is made in LibreOffice Impress, using candyclone template.
You can download the Impress document from a page in here:
With this downloadable document, you can use the style of this presentation, for use with your own presentation works, either for school material, office works, homeworks, or anything else.
You can also download the exported pdf from a page in here:
The pdf version cannot contain animation. So the content might be little different, compared with the original Impress document.
Inkscape
The Impress pages also utilize diagram illustration made in Inkscape. I also provide the source image in SVG format, that you can download from a page in here:
Here is the preview.
I intentionally share the source SVG image, so you can alter the content for your own personal use. I know there are already so many stock images for presentation, I just need to share, what I have, with tutorial. This way, anyone can make pretty presentation easier. Of course you still have to learn Inkscape, to suit the illustration for your own use.
Template
What is this candyclone rubbish?
Candyclone is an Impress template that I have made for LibreOffice contest.
There are also other free templates as well in lumbung repository.
This candyclone is just an example template that you can use freely. With this candyclone example you can also learn how to make your own template. Your very own template to suit your ecosystem.
Disagreement
What if I do not agree?
The source is available, so you can freely make your own slide. Feel free to express your thoughts, either with text, or illustration.
The Slides
Here I represent all the slides.
Slide 01: Cover

Learning Linux Diversity
Dive into Linux Subsystem for Personal Educational Purpose.
Slide 02: About The Author
I have my own blog.
Slide 03: About This Material

After watching this, you will understand:
- A more systematic steps to learn GNU/linux.
- How to make your own learning plan (syllabus).
This material is not really comprehensive. I still have so much to learn.
Slide 04: Chapter Break

Slide 05: After First Linux Install

You might desire to:
- Join linux community.
- Read documentation (statistically rare person).
- Update system.
- Install a bunch of application.
- Get busy with command line terminal.
- Surfing wiki and search engine.
And then what?
Slide 06: Where to Go from Here

Where to go from here?
- Should I try other distro?
- What other distro should I try?
- So many distro, so little differences!
- Should I use VM or multiboot?
Learn part of system! Instead of just switching distro.
Slide 07: Chapter Break
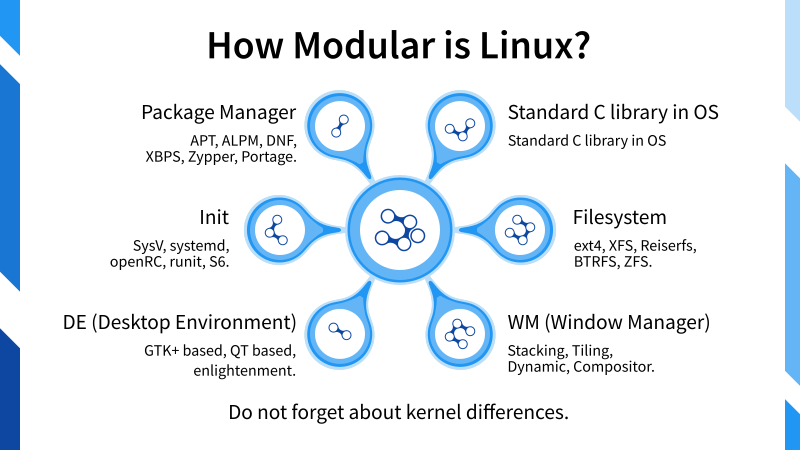
Slide 08: How Modular is Linux?
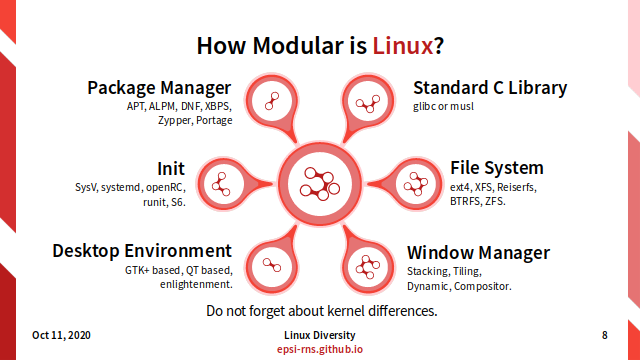
How Modular is Linux?
- Package Manager:
- APT, ALPM, DNF, XBPS, Zypper, Portage.
- Init:
- SysV, systemd, openRC, runit, S6.
- Filesystem:
- ext4, XFS, Reiserfs, BTRFS, ZFS.
- Standard C library in OS:
- glibc or musl.
- DE (Desktop Environment):
- GTK+ based, QT based, enlightenment.
- WM (Window Manager):
- Stacking, Tiling, Dynamic, Compositor.
Local Groups:
-
Init: Init Freedom
-
Desktop Environment: Desktop Environment Indonesia
-
Window Manager: Dotfiles Indonesia
-
Learning GNU/Linux: Belajar GNU/Linux Indonesia
Slide 09: Three Diversity

You still need to Switch distro, by considering these three diversity:
-
Package Manager,
-
File system,
-
Init.
Slide 10: When do I need a physical OS?

When do I need a physical OS?
- You can learn Package Manager using Docker.
- You can also learn Init using Docker.
- But you cannot learn Filesystem using Docker.
File system experience require long time examination. Thus you have to live with baremetal (physical) OS.
Slide 11: Desktop Environment/ Window Manager

Yet Another Presentation.
Most beginner start from switching DE/WM:
Slide 12: Common Subsystem?

Links:
Slide 13: Chapter Break

Slide 14: Docker Test Bed

You can utilize docker to learn other package manager.
- APT, ALPM, DNF, XBPS, Zypper, Portage.
Docker - Package Management Summary
Docker is suitable for old notebook with low resources.
Slide 15: More Articles about Docker Test Bed
Links:
Slide 16: Package Manager Feature

Slide 17: Package Manager Advantage/Issue

Links:
Deep knowledge require long time experience. Most of issues comes months after install.
Slide 18: Chapter Break

Slide 19: Init: Who use what
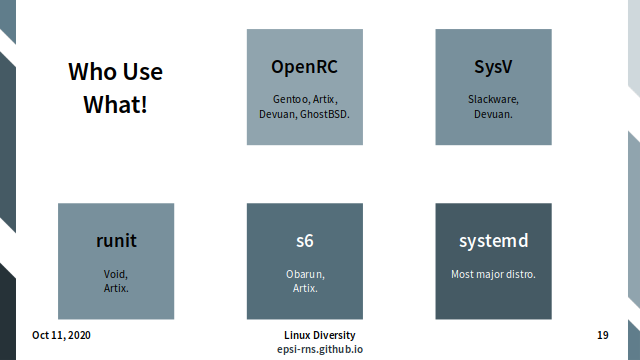
Who use what.
- OpenRC: Gentoo, Artix, Devuan.
- runit: Void, Artix.
- s6: Obarun, Artix.
- SysV: Slackware, Devuan.
- systemd: Most Major Distro
Slide 20: Init Civil War

Link:
The systemd Controversy: Still debating in 2020 between: systemd+gnome versus linux+diversity.
Slide 21: Init Elements
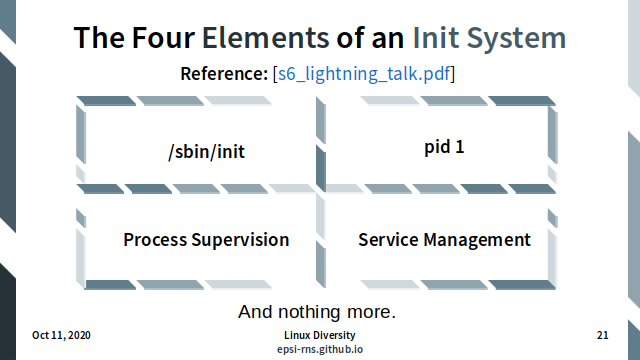
Reference:
The four elements of an init system:
/sbin/initpid 1Process SupervisionService Management
And nothing more.
Slide 22: Example Usage of Init

Link:
Slide 23: Chapter Break: File System

File System: ext4, XFS, Reiserfs, BTRFS, ZFS.
Deep knowledge require long time experience. Most of issues comes months after install. You cannot just install, and just understand file system instantly.
Slide 24: File System, and How to Find It.
File System, and How to Find It.
- ext4: most common in linux.
- ZFS: common in BSD.
- UFS: common in BSD.
- BRTRFS: Default in openSUSE
/. - XFS: can be installed in most linux.
Slide 25: Filesystem: Example Issues and Workarounds
Links:
Slide 26: Standard C library in OS?

glibc or musl.
I must admit, I do not have any experiece with musl.
Slide 27: Chapter Break

Slide 28: Switching Distro: Custom Plan

While you are young and still have time. Get yourself quarterly (three months) curriculum/plan.
Just get pass through it. No need to go deep with coding. Be an ordinary user.
After this one year, you are already mature enough with broader view to choose whatever linux you want.
If you want to get more wisdom. Learn BSD land in the second year.
Slide 29: Switching Distro: Example Syllabus
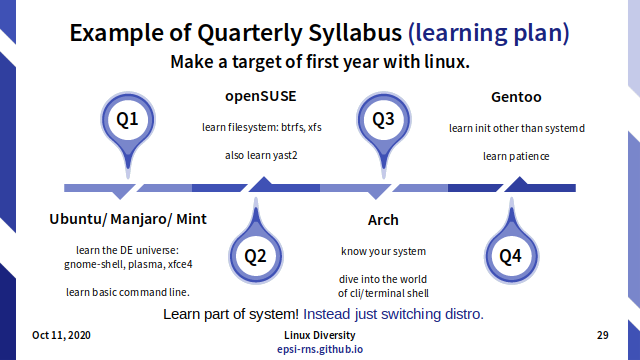
Example Syllabus (learning plan):
Make a target of first year with linux.
- Q1: ubuntu/mint/manjaro
- learn the DE universe: gnome-shell, plasma, xfce4
- learn basic command line.
- Q2: opensuse
- learn filesystem: btrfs, xfs
- also learn yast2
- Q3: arch
- know your system, dive into the world of cli/terminal shell.
- Q4: gentoo
- learn init other than systemd
- learn patience
Slide 30: Switching Distro: First Quarter
Manuals:
Example Q1: Ubuntu/ Mint/ Manjaro
- Basic Terminal Command
- ls, cat, grep, ps, top, man, info, su, sudo
- always use $ man for documentation before google.
- Also learn about basic linux briefly
- Examine Filesystem Hierarchy Standard (FHS)
- Examine boot process.
- Solving audio or wireless issue.
- Read The Fine Manual
- ubuntu-manual
- debian-handbook (hertzog)
- More Terminal Command
- nmcli, ncdu, ntop, cfdisk
- lspci, lsusb, lsmod, dmesg, ip, iw
Slide 31: Switching Distro: Third Quarter
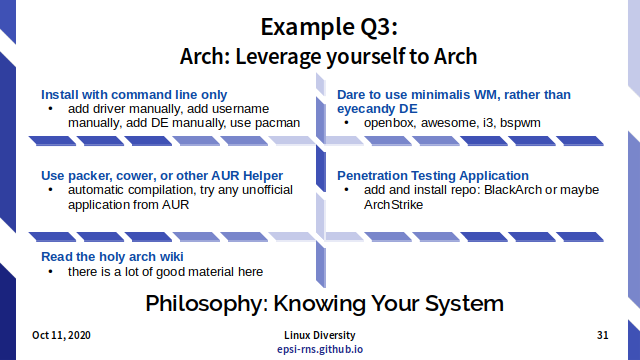
Example Q3: Arch: Leverage yourself to Arch
- Install with command line only
- add driver manually, add username manually, add DE manually, use pacman.
- Read the holy arch wiki
- there is a lot of good material here
- Use packer, cower, or other AUR Helper
- automatic compilation, try any unofficial application from AUR
- Dare to use minimalis WM, rather than eyecandy DE
- openbox, awesome, i3, bspwm
- Penetration Testing Application
- add and install repo: BlackArch or maybe ArchStrike
Philosophy: Knowing Your System
Slide 32: Switching Distro: Install Log/ Post Install Log
Links: Install Log/ Post Install Log:
Slide 33: Chapter Break

Slide 34: Partition Schema using MBR (old example)
Link:
For linux enthusiast.
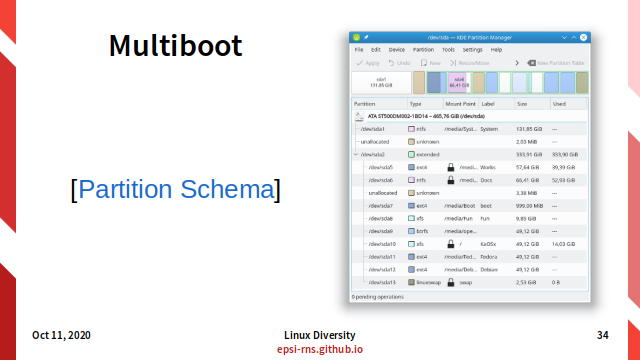
Slide 35: Multiboot: Using MBR (old schema)
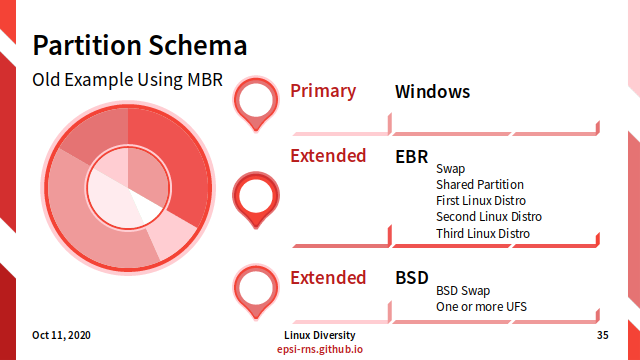
Partition Schema using MBR (old example)
-
Primary: Windows
- Extended: EBR
- Linux Swap
- Shared Partition
- First Linux Distro
- Second Linux Distro
- Third Linux Distro
- Extended: BSD
- BSD Swap
- One or more UFS
Slide 36: Multiboot - /etc/fstab
Link:
/etc/fstab
- Learn to make shared partition.
- BTRFS subvolume is interesting.
Slide 37: Multiboot: chroot
Link:
chroot
- Some OS is comfortably installed using chroot:
- such as: Gentoo, LFS.
- Other OS can be updated using chroot:
- beware of small issues.
Slide 38: Multiboot: Tips: Samba Share
Link:
Tips: Keep your samba’s network share persistence along multiboot.
Slide 39: Multiboot - Tips: FreeBSD
Link:
Tips: Linux Multiboot with BSD, can be done using UFS, instead of ZFS.
Slide 40: Kernel

make menuconfig
Slide 41: Chapter Break

Slide 42: Interesting Diversity: Example
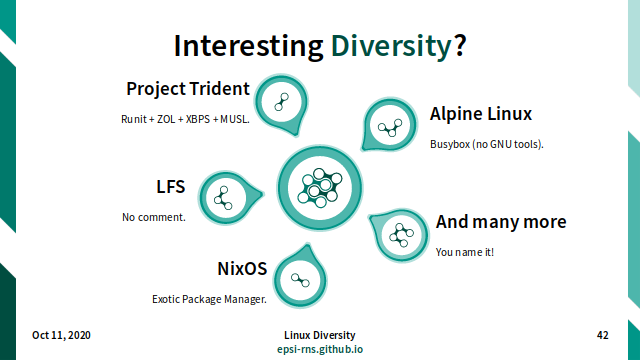
Interesting Diversity?
- Project Trident
- runit + zol + xbps + musl
- Alpine Linux
- Busybox (no GNU tools)
- NixOS
- Exotic Package Manager
- LFS
- No comment.
- And many more
- You name it!
Slide 43: What’s Next?

More Wisdom!
Learn BSD land!
Slide 44: Questions

Don’t be shy!
Slide 45: Thank You
Thank you for your time.