Preface
Goal: Separate Main Flow, Code, and Data.
So anyone can focus to alter special customization in Main Script, without changing the whole stuff.
Reading
Before you jump off to scripting, you might desire to read this overview.
All The Source Code:
Impatient coder like me, like to open many tab on browser.
Table of Content
-
Preface: Table of Content
-
3: System Calls
-
6: Hash: Config
-
10: Run Baby Run
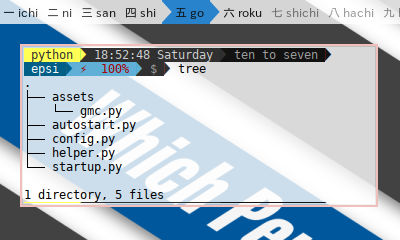
1: Directory Structure
Directory Structure has been explained in preface.
This figure will explain how it looks
in Python script directory.
2: Modularizing in Python
Nothing to say here. Python is simple
Declare a module
No need to explicitly define what to export.
Here we export hc function variable from helper module.
Nothing to write in Python Module
Call a module
import helper
from helper import hc3: System Calls
Here we wrap herbstclient system call
in a function named hc.
helper.py
def hc(arguments):
os.system("herbstclient "+arguments)autostart.py
# Read the manual in $ man herbstluftwm
hc('emit_hook reload')
# gap counter
os.system("echo 35 > /tmp/herbstluftwm-gap");4: List: Tag Names and Keys
config.py
tag_names = list(range(1, 10))
tag_keys = list(range(1, 10)) + [0]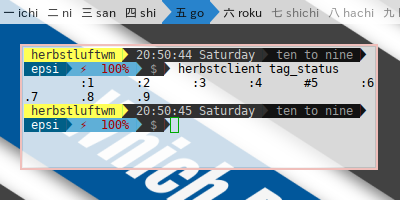
5: Hash: Color Schemes
Using key-value pairs, a simple data structure.
gmc.py
color = {
'white' : '#ffffff',
'black' : '#000000',
'grey50' : '#fafafa',
'grey100' : '#f5f5f5'
}autostart.py
# background before wallpaper
os.system("xsetroot -solid '"+color['blue500']+"'")View Source File:
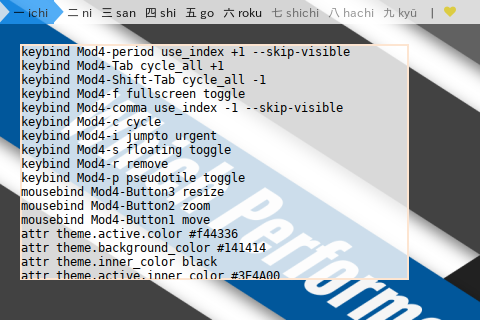
6: Hash: Config
The Hash in Config is very similar with the colors above. Except that it has string concatenation all over the place.
config.py
# Modifier variables
s = 'Shift'
c = 'Control'
m = 'Mod4'
a = 'Mod1'
keybinds = {
# session
m+'-'+s+'-q' : 'quit',
m+'-'+s+'-r' : 'reload',
m+'-'+s+'-c' : 'close'
}This config will be utilized in main script as shown in the following code.
autostart.py
helper.do_config("keybind", config.keybinds)
helper.do_config("keybind", config.tagskeybinds)
helper.do_config("mousebind", config.mousebinds)
helper.do_config("attr", config.attributes)
helper.do_config("set", config.sets)
helper.do_config("rule", config.rules)View Source File:
7: Processing The Hash Config
This is the heart of this script.
This do-config function has two arguments,
the herbstclient command i.e “keybind”, and hash from config.
I can see how simple and clean, Python is.
helper.py
def do_config(command, dictionary):
# loop over dictionary
for key, value in dictionary.items():
hc(command+' '+key+' '+value)
# uncomment to debug in terminal
# print(command+' '+key+' '+value)Debug Herbstclient Command
I do not remove line where I do debug when I made this script, so anyone can use it later, avoid examining blindly. Sometimes strange things happen. Just uncomment this line to see what happened.
print(command+' '+key+' '+value)You can see the debugging result in figure below.
View Source File:
8: Setting the Tags
Python use from import mechanism.
helper.py
import config
from config import tag_names, tag_keysdef set_tags_with_name():
hc("rename default '" + str(tag_names[0]) + "' 2>/dev/null || true")
for index, tag_name in enumerate(tag_names):
hc("add '" + str(tag_names[index]) + "'")
key = tag_keys[index];
if key:
hc("keybind Mod4-" + str(key)
+ " use_index '" + str(index) + "'")
hc("keybind Mod4-Shift-" + str(key)
+ " move_index '" + str(index) + "'")9: Launch the Panel
Two more functions left, it is do_panel
and startup_run.
This two also be easy to do in Python.
helper.py
def do_panel():
dirname = os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__))
panel = dirname + "/panel-lemonbar.py"
if not os.path.isfile(panel) and os.access(panel, os.X_OK):
panel = "/etc/xdg/herbstluftwm/panel.sh"
raw = os.popen('herbstclient list_monitors | cut -d: -f1').read()
monitors = raw.strip().split("\n")
for monitor in (monitors):
os.system(panel + ' ' + str(monitor) + ' &');10: Run Baby Run
This is the last part. It is intended to be modified. Everyone has their own personal preferences.
startup.py
def run():
command = 'silent new_attr bool my_not_first_autostart'
exitcode = os.system('herbstclient ' + command)
if exitcode == 0:
# non windowed app
os.system("compton &")
os.system("dunst &")
os.system("parcellite &")
os.system("nitrogen --restore &")
os.system("mpd &")
# windowed app
os.system("xfce4-terminal &")
os.system("sleep 1 && firefox &")
os.system("sleep 2 && geany &")
os.system("sleep 2 && thunar &")View Source File:
11: Putting It All Together
The last part is going to main script and putting it all back together.
Now the flow is clear
Header Part: autostart.py
import os
from gmc import color
import helper
from helper import hc
import config
from config import tag_names
import startupProcedural Part: autostart.py
# background before wallpaper
os.system("xsetroot -solid '"+color['blue500']+"'")
# Read the manual in $ man herbstluftwm
hc('emit_hook reload')
# gap counter
os.system("echo 35 > /tmp/herbstluftwm-gap");
# do not repaint until unlock
hc("lock");
# standard
hc('keyunbind --all')
hc("mouseunbind --all")
hc("unrule -F")
helper.set_tags_with_name()
# do hash config
helper.do_config("keybind", config.keybinds)
helper.do_config("keybind", config.tagskeybinds)
helper.do_config("mousebind", config.mousebinds)
helper.do_config("attr", config.attributes)
helper.do_config("set", config.sets)
helper.do_config("rule", config.rules)
# unlock, just to be sure
hc("unlock")
# launch statusbar panel
helper.do_panel()
# load on startup
startup.run()View Source File:
Coming up Next
After the Window Manager, comes the Panel.
Happy Configuring.